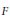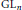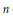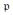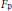Refine search
Actions for selected content:
23 results
5 - Designing the Global Building Network: A Case for People-Centered Energy Education
-
-
- Book:
- Energy Education in a Transitioning World
- Published online:
- 08 January 2026
- Print publication:
- 19 January 2026, pp 93-109
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 2 - Public and Private Interests
-
- Book:
- The State, the Law, and the People in the Roman Empire
- Published online:
- 11 December 2025
- Print publication:
- 11 December 2025, pp 64-118
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Urban Preservation
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
7 - Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency in Circular Economy Liveable Cities
-
-
- Book:
- The Circular Economy and Liveable Cities
- Published online:
- 05 September 2025
- Print publication:
- 04 September 2025, pp 101-111
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Building energy demand pathways for reaching a net-zero carbon society
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Energy Transitions / Volume 1 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2025, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
10 - On Architecture’s Agency in Fourth-Century Rome
- from Part III - Architecture and Art
-
-
- Book:
- Making the Middle Republic
- Published online:
- 20 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 27 April 2023, pp 210-229
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 26 - Drawing Chicago: Chris Ware’s Graphic City
- from Part V - Traditions and Futures: Contemporary Chicago Literatures
-
-
- Book:
- Chicago
- Published online:
- 02 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 23 September 2021, pp 370-386
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction: Memory, Family, and Community in Roman Ephesos
-
- Book:
- Memory, Family, and Community in Roman Ephesos
- Published online:
- 06 July 2021
- Print publication:
- 15 July 2021, pp 1-9
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Memory, Family, and Community in Roman Ephesos
-
- Published online:
- 06 July 2021
- Print publication:
- 15 July 2021
3 - Defying a Defining Witness: the Bronze Horseman and the Buildings (De Aedificiis) of Prokopios
-
- Book:
- The Bronze Horseman of Justinian in Constantinople
- Published online:
- 08 April 2021
- Print publication:
- 29 April 2021, pp 72-97
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
2 - The Making of Justinian’s Forum
-
- Book:
- The Bronze Horseman of Justinian in Constantinople
- Published online:
- 08 April 2021
- Print publication:
- 29 April 2021, pp 38-71
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
THE CASTLE OF ACHANDUIN, LISMORE—A POINT OF REFERENCE FOR THE RADIOCARBON ANALYSIS OF MORTAR-ENTRAPPED RELICT LIMEKILN FUELS
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 62 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2020, pp. 1563-1575
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Frugality, Building, and Heirlooms in an Age of Social Mobility
-
-
- Book:
- Roman Frugality
- Published online:
- 26 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 347-371
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - Material Religious Culture
-
- Book:
- English Convents in Catholic Europe, c.1600–1800
- Published online:
- 20 December 2019
- Print publication:
- 02 January 2020, pp 78-98
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Buildings, spiders, and geometric Satake
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 149 / Issue 11 / November 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2013, pp. 1871-1912
- Print publication:
- November 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overview of Actions Taken by Hellenic National Centre for Emergency Care Responding to the 07 September 1999 Earthquake in Athens
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 20 / Issue S1 / April 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2012, pp. 4-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
AN EIGENSPACE OF LARGE DIMENSION FOR A HECKE ALGEBRA ON AN
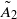 BUILDING
BUILDING
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 91 / Issue 1 / August 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2011, pp. 29-54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Application of the Bruhat-Tits tree of SU3(h) to some Ã2 groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / June 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 329-344
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Hypergraph with Commuting Partial Laplacians
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / 01 December 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 385-397
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2001
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
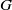
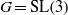
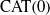
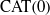
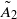 BUILDING
BUILDING
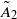 and let 𝔸 be its fundamental apartment. We consider the set 𝕌
and let 𝔸 be its fundamental apartment. We consider the set 𝕌