Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6993 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Correction of finite difference eigenvalues of periodic Sturm-Liouville problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / April 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 460-469
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Complementary variational principles for a class of nonlinear boundary value problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / April 1979
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 102-112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Global attractivity in differential equations with variable delays
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 568-579
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / January 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, p. 288
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stability of non-linear systems with time-varying delays
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / April 1980
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 452-463
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A note on the singularities in the theory of water waves with an inertial surface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / October 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 271-278
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ordinary and partial difference equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / April 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 488-501
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Accelerated spectral refinement Part II: Cluster of eigenvalues
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / October 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 224-243
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 39 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / July 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Combustion waves with reactant depletion
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / July 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 119-135
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Chaos in perturbed Lotka-Volterra systems
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / January 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 399-412
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the scattering of water waves by a submerged slender barrier
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / October 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 171-189
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Existence of seamount steady vortex flows
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 1 / July 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 75-88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Degenerate bifurcations near a double eigenvalue in the Brusselator
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / April 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 486-535
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Control systems with time lags
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / December 1976
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 478-492
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Computation of critical parameters for a problem in combustion theory
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / July 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 40-46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The method of the hypercircle for a class of nonlinear equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / April 1979
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 75-83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Bow flows with smooth separation in water of finite depth
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 1 / July 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 114-126
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The diffraction of long elastic waves by elliptic cylindrical cavities
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / July 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 108-118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nonlinear model reference adaptive control
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / October 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 147-157
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
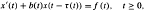
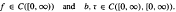
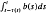 is asymptotically constant.
is asymptotically constant.