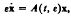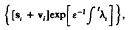Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Determining rotational deformity in broken forearms
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 561-568
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 40 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 19 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 3 / June 1976
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Multigrid methods for the biharmonic equation using some nonconforming plate elements
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / October 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 279-289
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Energy flux for plane waves in linear conservative systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / June 1977
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 106-113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A completely monotonic function involving the divided difference of the psi function and an equivalent inequality involving sums
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 48 / Issue 4 / April 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 523-532
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Diffusion theory can be applied to antibodies attaching to ligand sites
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 4 / April 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 495-505
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Solution of the problem of scattering of water waves by a nearly vertical plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / January 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 382-395
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 20 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / June 1978
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 29 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / April 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Reflection coefficients and energy ratios in a micropolar thermoelastic medium without energy dissipation
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 48 / Issue 3 / January 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 433-447
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Supplementary variable method applied to the MAP/G/1 queueing system
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / July 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 86-96
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Necessary optimality conditions for bicriterion discrete optimal control problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / January 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 392-402
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A functional differential equation arising in modelling of cell growth
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / April 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 424-435
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stiff systems of ordinary differential equations. Part 1. Completely stiff, homogeneous systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / July 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 17-51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Hilbert inequality and an Euler-Maclaurin summation formula
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 48 / Issue 3 / January 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 419-431
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Surface mounted heat flux sensors
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 27 / Issue 3 / January 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 281-294
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Existence of optimal controls for semilinear elliptic equations without Cesari-type conditions
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / July 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 115-131
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 30 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / July 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 31 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / July 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
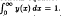 We first look at a number of properties that any solution of this equation and boundary condition must have, and then proceed to find the unique solution by the method of Laplace transforms. Results from number theory on the infinite product found in the solution are presented, and it is shown that
We first look at a number of properties that any solution of this equation and boundary condition must have, and then proceed to find the unique solution by the method of Laplace transforms. Results from number theory on the infinite product found in the solution are presented, and it is shown that