Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6993 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Flowshop/no-idle scheduling to minimise the mean flowtime
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 2 / October 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 265-275
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 29 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / January 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ship bows with contiunous and splashless flow attachment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / April 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 442-452
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Two-dimensional resonators with small openings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / July 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 2-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Inversion of the Struve transform of half integer order
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 2 / October 1983
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 161-174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stiff systems of ordinary differential equations. III. Partially stiff systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / January 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 310-331
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A convergence theorem for singular integral equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 22 / Issue 4 / April 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 539-552
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 43 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / January 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Synthesis of layered shells from a finite set of viscoelastic materials
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 525-534
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Two infinite-Froude-number cusped free-surface flows due to a submerged line source or sink
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / October 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
General iterative methods for nonlinear boundary value problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / July 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 58-85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Eigenvalue characterization for (n · p) boundary-value problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / January 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 386-407
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Numerical integration of the RLW equation using cubic splines
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 1 / July 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 131-142
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Series operations using minimum storage
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / April 1979
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 84-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The commutation relation i[Y, Z] = 2Y and the absolutely continuous spectrum of Y
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / April 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 420-427
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The sputtering temperature of a cooling cylindrical rod without and with an insulated core in a two-fluid medium
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / July 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 87-100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The transition through resonance of a nonlinear non-autonomous system
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / July 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 81-111
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A robust linearisation scheme for a nonlinear elliptic boundary value problem: Error estimates
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 4 / April 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 449-470
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Computer-controlled variable-structure systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / July 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
New algorithms for discrete-time optimal control problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 26 / Issue 2 / October 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 129-145
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
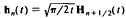 we show that the Struve transform of half integer order, or spherical Struve transform,
we show that the Struve transform of half integer order, or spherical Struve transform,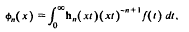
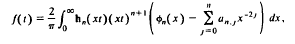
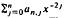 is the sum of the first
is the sum of the first 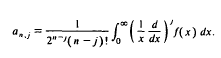
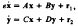
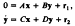
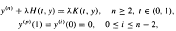
 on
on 