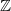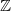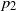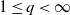Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52653 results in Statistics and Probability
32 - Value Loss
- from V - Global Optimisation
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 259-266
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
21 - Uncertainty Calibration
- from III - Linear Algebra
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 175-182
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp i-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
22 - Proofs
- from III - Linear Algebra
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 183-192
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
VIII - Solutions to Exercises
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 357-368
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp vi-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
30 - Introduction
- from V - Global Optimisation
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 247-250
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
31 - Bayesian Optimisation
- from V - Global Optimisation
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 251-258
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp vii-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
2 - Probabilistic Inference
- from I - Mathematical Background
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 21-22
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Probabilistic Numerics
- Published online:
- 01 June 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2022, pp 223-398
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Scalable algorithms for physics-informed neural and graph networks
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2022, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli from shrimp and salmon available for purchase by consumers in Canada: a risk profile using the Codex framework
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2022, e148
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The incidence of Orientia tsutsugamushi infection in rural South India
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2022, e132
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coexistence of lazy frogs on
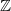 ${\mathbb{Z}}$
${\mathbb{Z}}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2022, pp. 702-713
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Liver function tests in primary care provide a key opportunity to diagnose and engage patients with hepatitis C
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2022, e133
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Discounted optimal stopping problems in first-passage time models with random thresholds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2022, pp. 714-733
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A value-at-risk approach to futures hedge
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2022, pp. 818-832
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mycoplasma genitalium and Chlamydia trachomatis infection among women in Southwest China: a retrospective study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2022, e129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Limit theorems for random points in a simplex
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2022, pp. 685-701
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation