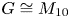Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1366291 results in Open Access
FLM volume 990 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 990 / 10 July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
INSIGHTS INTO PHARAONIC EGYPT - (R.) Bussmann The Archaeology of Pharaonic Egypt. Society and Culture, 2700–1700 bc. Pp. xiv + 426, figs, ills, maps. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. Cased, £100, US$130. ISBN: 978-1-107-03038-1.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 507-509
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of occurrence of Amblyseius andersoni (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on two native phytoseiid (Mesostigmata) mites in a Japanese apple (Rosacaea) orchard
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 156 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, e18
-
- Article
- Export citation
The insect colonisation, succession, and decomposition of the domestic pig (Artiodactyla: Suidae) in southern Ontario, Canada
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 156 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Marlborough Mound: prehistoric mound, medieval castle, Georgian garden. Edited by Richard Barber. 235mm. Pp xi + 221, 51 + 3 figs (some col). The Boydell Press, Woodbridge, 2022. isbn 9781783271863. £45 (hbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Antiquaries Journal / Volume 104 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 392-393
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rethinking the Frontline - Guerillas and Combative Mothers: Women and the Armed Struggle in South Africa Siphokazi Magadla. Pietermaritzburg, South Africa: University of KwaZulu-Natal, 2023. Pp. 222. R300, paperback (ISBN: 9781869145163).
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 121-122
-
- Article
- Export citation
Decision Making in a Strategic Medical Command and Control Team During the Covid-19 Pandemic: A Case Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, e119
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimizing surface properties in pure titanium for dental implants: a crystallographic analysis of sandblasting and acid-etching techniques
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 39 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 206-216
-
- Article
- Export citation
China's Rising Foreign Ministry: Practices and Representations of Assertive Diplomacy Dylan M. H. Loh. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2024. 240 pp. $75.00 (hbk). ISBN 9781503638204
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 260 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1097-1098
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Words like Water: Queer Mobilization and Social Change in China Caterina Fugazzola. Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press, 2023. 168 pp. $25.95 (pbk). ISBN 9781439921470
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 260 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1124-1126
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Media Credibility and Voter Penalization of Corrupt Politicians in Latin America
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 40-57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Miscegenation Madness: Interracial Intimacy and the Politics of ‘Purity’ in Twentieth-Century South Africa
-
- Journal:
- Du Bois Review: Social Science Research on Race / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / Fall 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 223-249
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Breakdown of Effective Field Theory in Particle Physics: Lessons for Understanding Intertheoretic Relations
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 92 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 100-120
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Old Wine in New Bottles, or Novel Challenges? A Labour History Perspective on Digital Labour
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 307-316
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The structure of finite groups whose elements outside a normal subgroup have prime power orders
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gary Chartier, Christianity and the Nation State: A Study in Political Theology (Cambridge: CUP, 2023), p. xviii + 324. $110.00
-
- Journal:
- Scottish Journal of Theology / Volume 77 / Issue 3 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 292-294
-
- Article
- Export citation
MILITARY WIVES THEN AND NOW - (E.) Bridges Warriors’ Wives. Ancient Greek Myth and Modern Experience. Pp. xii + 234. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2023. Cased, £25, US$35. ISBN: 978-0-19-884352-8.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 262-264
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A flow-field integrated flight control: dynamic wind tunnel testing and simulation
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1329 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 2451-2482
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation