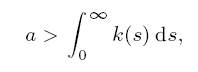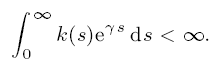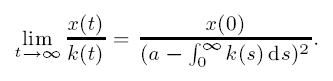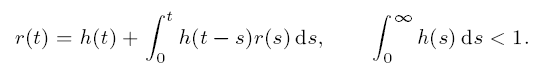Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25845 results in Abstract analysis
References
-
- Book:
- Harmonic Maps, Conservation Laws and Moving Frames
- Published online:
- 13 August 2009
- Print publication:
- 13 June 2002, pp 254-262
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Non-linear boundary value problems on the semi-infinite interval: an upper and lower solution approach
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 129-140
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterizations of a two dimensional Euclidean ring among near-rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 59-64
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Remarks on the asymptotic behaviour of solutions to the compressible Navier–Stokes equations in the half-line
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 627-638
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
The longest segment in the complement of a packing
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 45-49
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
The universal quaternary quadratic form with the maximal discriminant
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 197-199
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
On minimal pairs and residually transcendental extensions of valuations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 93-106
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homogenization of a neutronic critical diffusion problem with drift
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 567-594
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Irreducible and end type group actions on Λ-trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 65-70
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
On integers which are not differences of two powers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 231-243
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Diffusive-dispersive travelling waves and kinetic relations. II A hyperbolic–elliptic model of phase-transition dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 545-565
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Universal attractors for a nonlinear one-dimensional heat-conductive viscous real gas
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 685-709
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Normal modes for a stratified viscous fluid layer
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 611-625
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiplicities of eigenvalues of a vector-valued Sturm-Liouville problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 119-127
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Subexponential solutions of linear integro-differential equations and transient renewal equations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 521-543
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hilbert function and fractional powers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 71-75
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the representation of an integer as the sum of a large and a small square
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 245-251
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Index to Volume 49
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, p. 263
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adjacency preserving maps on matrices and operators
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 661-684
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rational homology of spaces of complex monic polynomials with multiple roots
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 49 / Issue 1-2 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2010, pp. 77-91
- Print publication:
- June 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
 of
of