Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25816 results in Abstract analysis
Existence and uniqueness of the global admissible solution for a viscoelastic model with relaxation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 5 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1113-1132
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Large-time asymptotic behaviour of a step for the Benjamin–Bona–Mahony–Burgers equation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1-18
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the number of nonorientable Wicks forms in a free group
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 113-116
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uniqueness, multiplicity and stability for positive solutions of a pair of reaction–diffusion equations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 4 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 777-809
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mean curvature and shape operator of isometric immersions in real-space-forms
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / January 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 87-97
- Print publication:
- January 1996
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sturm–Liouville problems with indefinite weights and Everitt's inequality
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 5 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1097-1112
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Solutions in the large for certain nonlinear parabolic equations and applications*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 19-45
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stable periodic solutions of a spatially homogeneous nonlocal reaction–diffusion equation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 4 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 867-884
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jacobi's elliptic functions and Lagrangian immersions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 4 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 687-704
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Congruences on orthodox semigroups with associate subgroups
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / January 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 113-124
- Print publication:
- January 1996
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The initial-value problem for the forced Korteweg-de Vries equation*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 3 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 571-598
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spectral asymptotics with a remainder estimate for Schrödinger operators with slowly growing potentials
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 4 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 829-836
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stability and instability of some nonlinear dispersive solitary waves in higher dimension
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 89-112
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
The limit of the anisotropic double-obstacle Allen–Cahn equation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1217-1234
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 126 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 5 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Least energy solutions for elliptic equations in unbounded domains
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 195-208
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 126 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 3 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stochastic generalised KPP equations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 5 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 957-983
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Regular and singular Sturm–Liouville problems with coupled boundary conditions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 3 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 505-514
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Positivity of solutions of elliptic equations with nonlocal terms*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 126 / Issue 3 / 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 643-663
- Print publication:
- 1996
-
- Article
- Export citation
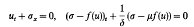
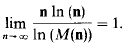
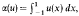 are considered together with Neumann or Dirichlet boundary conditions. One of the main results deals with linearisation at equilibria. It states that, for any given set of complex numbers, one can arrange, choosing the equation properly, that this set is contained in the spectrum of the linearisation. The second main result shows that equations of the above form can undergo a supercritical Hopf bifurcation to an asymptotically stable periodic solution.
are considered together with Neumann or Dirichlet boundary conditions. One of the main results deals with linearisation at equilibria. It states that, for any given set of complex numbers, one can arrange, choosing the equation properly, that this set is contained in the spectrum of the linearisation. The second main result shows that equations of the above form can undergo a supercritical Hopf bifurcation to an asymptotically stable periodic solution.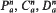 and two exceptional Lagrangian submanifolds
and two exceptional Lagrangian submanifolds 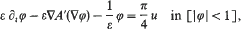
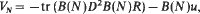
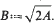 More precisely, we show that the Hausdorff-distance between the zero-level set of
More precisely, we show that the Hausdorff-distance between the zero-level set of 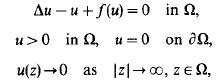
 , the solutions of the stochastic generalised KPP equations converge to deterministic approximate travelling waves and if
, the solutions of the stochastic generalised KPP equations converge to deterministic approximate travelling waves and if
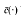 being an associated potential energy, Ф
being an associated potential energy, Ф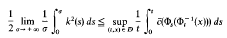
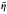 and 0 >
and 0 >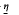 such that for all
such that for all 