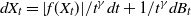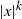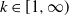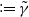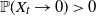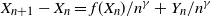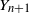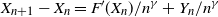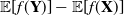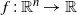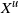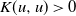Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52669 results in Statistics and Probability
Continuum line-of-sight percolation on Poisson–Voronoi tessellations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 510-536
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
One-dimensional system arising in stochastic gradient descent
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 575-607
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
A generalised Dickman distribution and the number of species in a negative binomial process model
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 370-399
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
A product form for the general stochastic matching model
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 449-468
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exact simulation of Ornstein–Uhlenbeck tempered stable processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 347-371
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
APR volume 53 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
APR volume 53 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ruin problems for epidemic insurance
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 484-509
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
JPR volume 59 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Weak convergence of stochastic integrals with respect to the state occupation measure of a Markov chain
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 372-393
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Population dynamics driven by truncated stable processes with Markovian switching
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 505-522
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stochastic orderings of multivariate elliptical distributions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 551-568
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Markov chain approximation of one-dimensional sticky diffusions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 335-369
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stochastic analysis of average-based distributed algorithms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 394-410
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
JPR volume 58 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JPR volume 59 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A class of solvable multidimensional stopping problems in the presence of Knightian uncertainty
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 400-424
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Couplings for determinantal point processes and their reduced Palm distributions with a view to quantifying repulsiveness
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 469-483
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exact simulation of the genealogical tree for a stationary branching population and application to the asymptotics of its total length
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 537-574
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Queues with path-dependent arrival processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 484-504
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation