Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52621 results in Statistics and Probability
Antibacterial resistance to antibiotics
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, e72
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular detection of Histoplasma capsulatum in organ samples from bats randomly captured in urban areas of Araraquara, São Paulo state, Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of nontuberculous mycobacteria and the emergence of rare species in Henan Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, e92
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Salmonella Saintpaul outbreak associated with cantaloupe consumption, the United Kingdom and Portugal, September to November 2023
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maximum chordal subgraphs of random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. 611-623
-
- Article
- Export citation
JPR volume 61 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
APR volume 56 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
THE ECONOMETRIC THEORY AWARDS 2024
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, p. 471
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JPR volume 61 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
APR volume 56 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A remark on exact simulation of tempered stable Ornstein–Uhlenbeck processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2024, pp. 1196-1198
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Learning-based augmentation of physics-based models: an industrial robot use case
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTICALLY UNIFORMLY MOST POWERFUL TESTS FOR UNIT ROOTS IN GAUSSIAN PANELS WITH CROSS-SECTIONAL DEPENDENCE GENERATED BY COMMON FACTORS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 1184-1209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Comparative epidemiology of bacteraemia in two ageing populations: Singapore and Denmark
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e74
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Turán problems in pseudorandom graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 583-596
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Open data, workplace relations law compliance, and digital regulation
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 6 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Central limit theorem for components in meandric systems through high moments
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 597-610
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The latent cognitive structures of social networks
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 12 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 202-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Recurrence and transience of a Markov chain on
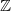 $\mathbb Z$+ and evaluation of prior distributions for a Poisson mean
$\mathbb Z$+ and evaluation of prior distributions for a Poisson mean
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 1361-1379
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
UK Asbestos Working Party Update 2020
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 29 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation