Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418957 results in Open Access
Layer-Charge Heterogeneity in Smectites of I-S Phases in Pelitic Sediments from the Molasse Basin, Austria
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 6 / December 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 670-678
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE
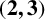 $\boldsymbol {(2,3)}$-GENERATION OF THE FINITE SIMPLE ODD-DIMENSIONAL ORTHOGONAL GROUPS
$\boldsymbol {(2,3)}$-GENERATION OF THE FINITE SIMPLE ODD-DIMENSIONAL ORTHOGONAL GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 117 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 130-148
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quadratic associations between cardiovascular stress reactivity and development of cool and hot executive functions in adolescents
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 664-677
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of Secondary Iron Phases on Kaolinite 27Al MAS NMR Spectra
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 4 / August 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 429-435
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Interaction of Polysaccharides with Silver Hill Illite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / April 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 151-156
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lead-210 Derived Sedimentation Rates from a North Louisiana Paper-Mill Effluent Reservoir
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 43 / Issue 5 / October 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 515-524
-
- Article
- Export citation
FTIR Study of Deuterated Montmorillonites: Structural Features Relevant to Pillared Clay Stability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / February 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 92-102
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis and Properties of Hexacyanoferrate Interlayered in Hydrotalcite. I. Hexacyanoferrate(II)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / April 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 170-179
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Electron Optical Investigation of the Alteration of Kaolinite to Halloysite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / April 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 212-229
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chemisorption of Benzene on Cu-Montmorillonite as Characterized by FTIR and 13C MAS NMR
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 41 / Issue 1 / February 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 87-94
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ca-Rectorite from Sano Mine, Nagano Prefecture, Japan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 45 / Issue 6 / December 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 773-780
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Al and Organic Acids on the Surface Chemistry of Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 4 / August 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 453-465
-
- Article
- Export citation
One-Step Synthesis of Alkyltrimethylammonium-Intercalated Magadiite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 224-229
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hard and Soft Acid-Base Model Applied to Bivalent Cation Selectivity on a 2:1 Clay Mineral
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 5 / October 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 546-555
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transmission Electron Microscopy Study of Very Low-Grade Metamorphic Rocks in Cambrian Sandstones and Shales, Ossa-Morena Zone, Southwest Spain
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 213-223
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transmission X-ray Diffraction Technique for Measuring Crystalline Swelling of Smectites in Electrolyte Solutions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / February 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 128-130
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mg-Smectite Authigenesis in a Marine Evaporative Environment, Salina Ometepec, Baja California
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / June 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 252-268
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forthcoming Papers
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 49 / Issue 5 / October 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, p. 453
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
57Fe Mössbauer Effect Study of Al-Substituted Lepidocrocites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / April 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 214-219
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rehydration of Zn-Al Layered Double Hydroxides
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / February 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 92-98
-
- Article
- Export citation