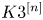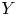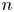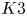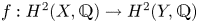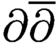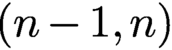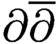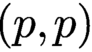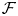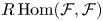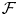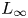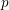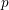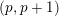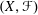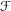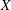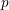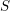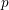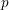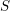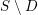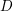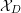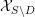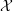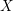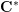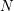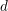Refine search
Actions for selected content:
18 results
Smoothing, scattering and a conjecture of Fukaya
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Pi / Volume 13 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2025, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
NON-LOG LIFTABLE LOG DEL PEZZO SURFACES OF RANK ONE IN CHARACTERISTIC FIVE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 259 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2025, pp. 399-422
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Deformations of morphisms of sheaves
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2025, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deformations of Calabi–Yau varieties with k-liminal singularities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2024, e59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rational Hodge isometries of hyper-Kähler varieties of
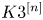 $K3^{[n]}$ type are algebraic
$K3^{[n]}$ type are algebraic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 160 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, pp. 1261-1303
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The moduli of sections has a canonical obstruction theory
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2022, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Group actions on local moduli space of holomorphic vector bundles
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2022, pp. 553-567
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Smoothing toroidal crossing spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Pi / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
POWER SERIES PROOFS FOR LOCAL STABILITIES OF KÄHLER AND BALANCED STRUCTURES WITH MILD
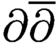 $\partial \overline {\partial }$-LEMMA
$\partial \overline {\partial }$-LEMMA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 246 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2021, pp. 305-354
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Formality conjecture for minimal surfaces of Kodaira dimension 0
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 157 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2021, pp. 215-235
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
On local stabilities of
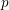 $p$-Kähler structures
$p$-Kähler structures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 155 / Issue 3 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2019, pp. 455-483
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Deformations of Pairs (Manifold, Coherent Sheaf)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 71 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2019, pp. 1209-1241
- Print publication:
- October 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON
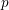 $p$-DIVISIBLE GROUPS WITH SATURATED NEWTON POLYGONS
$p$-DIVISIBLE GROUPS WITH SATURATED NEWTON POLYGONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 232 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2017, pp. 96-120
- Print publication:
- December 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A finiteness theorem on symplectic singularities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2016, pp. 1225-1236
- Print publication:
- June 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cohomology jump loci of differential graded Lie algebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 8 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2015, pp. 1499-1528
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Moduli of products of stable varieties
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 149 / Issue 12 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2013, pp. 2036-2070
- Print publication:
- December 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hilbert schemes and Betti numbers over Clements–Lindström rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 148 / Issue 5 / September 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2012, pp. 1337-1364
- Print publication:
- September 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Oort groups and lifting problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 144 / Issue 4 / July 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2008, pp. 849-866
- Print publication:
- July 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation





 introduced in [8]. Then a comparison between this tropicalized algebra with the dgBV algebra associated to the deformation theory of the semiflat part
introduced in [8]. Then a comparison between this tropicalized algebra with the dgBV algebra associated to the deformation theory of the semiflat part