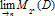Refine search
Actions for selected content:
21 results
Key predictors of prolonged overall treatment time in head and neck cancer radiotherapy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice / Volume 24 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2025, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Minimal H-factors and covers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2025, pp. 136-152
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rank-one non-singular actions of countable groups and their odometer factors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2024, pp. 1078-1128
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Understanding the development of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder in young people: a meta-review of systematic reviews
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 16 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, pp. 3769-3782
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The relationship between predisposing factors, premorbid function and symptom dimensions in psychosis: an integrated approach
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 17 / Issue 6 / October 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, pp. 311-320
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factors affecting burden of main caregivers in children with epilepsy
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 33 / Issue S1 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. S130-S131
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 - Algebra
-
- Book:
- The Student's Introduction to <I>Mathematica</I> and the Wolfram Language
- Published online:
- 01 April 2019
- Print publication:
- 16 May 2019, pp 145-190
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
17 - Unreliable Reliability: The Problem of Cronbach’s Alpha
- from Part II - How to Use Statistics
-
- Book:
- Doing Better Statistics in Human-Computer Interaction
- Published online:
- 26 January 2019
- Print publication:
- 07 February 2019, pp 204-213
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
16 - The Meaning of Factors
- from Part II - How to Use Statistics
-
- Book:
- Doing Better Statistics in Human-Computer Interaction
- Published online:
- 26 January 2019
- Print publication:
- 07 February 2019, pp 186-203
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Uniqueness of the von Neumann Continuous Factor
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 70 / Issue 5 / 01 October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 961-982
- Print publication:
- 01 October 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
11 - Leading change
-
- Book:
- Leadership
- Published online:
- 16 April 2019
- Print publication:
- 17 September 2018, pp 280-304
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 9 - Acute gastrointestinal conditions
-
- Book:
- Acute Care Nursing
- Published online:
- 12 December 2018
- Print publication:
- 01 August 2018, pp 168-189
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 8 - Acute neurological conditions
-
- Book:
- Acute Care Nursing
- Published online:
- 12 December 2018
- Print publication:
- 01 August 2018, pp 145-167
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 10 - Acute endocrine conditions
-
- Book:
- Acute Care Nursing
- Published online:
- 12 December 2018
- Print publication:
- 01 August 2018, pp 190-211
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Acute cardiovascular conditions
-
- Book:
- Acute Care Nursing
- Published online:
- 12 December 2018
- Print publication:
- 01 August 2018, pp 102-122
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 11 - Acute reproductive disorders
-
- Book:
- Acute Care Nursing
- Published online:
- 12 December 2018
- Print publication:
- 01 August 2018, pp 212-235
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Sketch of a componential subtheory of human intelligence
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 3 / Issue 4 / December 1980
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2010, pp. 573-584
-
- Article
- Export citation
General Laws of Adaptation to Environmental Factors:from Ecological Stress to Financial Crisis
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena / Volume 4 / Issue 6 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2009, pp. 1-53
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON SOME NORMING PROPERTIES OF SUBFACTORS
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / June 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2005, pp. 499-506
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation






 of cofinite subgroups in
of cofinite subgroups in