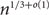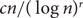Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6974 results in Algorithmics, Complexity, Computer Algebra, Computational Geometry
Improved Ramsey-type results for comparability graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, pp. 747-756
-
- Article
- Export citation
Robustness of randomized rumour spreading
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2020, pp. 37-78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A quantitative Lovász criterion for Property B
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 29 / Issue 6 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2020, pp. 956-960
-
- Article
- Export citation
Approximately counting bases of bicircular matroids
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2020, pp. 124-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the subgraph query problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2020, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Large triangle packings and Tuza’s conjecture in sparse random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2020, pp. 757-779
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pseudorandom hypergraph matchings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 29 / Issue 6 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2020, pp. 868-885
-
- Article
- Export citation
A note on distinct distances
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2020, pp. 650-663
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp xiii-xvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
6 - Selection
- from Part Two - Divide and Conquer
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 121-140
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
9 - Greedy algorithms on graphs
- from Part Three - Greedy Algorithms
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 205-236
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Greedy algorithms on lists
- from Part Three - Greedy Algorithms
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 145-176
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - Useful data structures
- from Part One - Basics
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 43-58
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part Six - Exhaustive Search
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 365-368
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part Four - Thinning Algorithms
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 237-240
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
11 - Segments and subsequences
- from Part Four - Thinning Algorithms
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 267-288
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp vii-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 432-437
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - Greedy algorithms on trees
- from Part Three - Greedy Algorithms
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp 177-204
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Algorithm Design with Haskell
- Published online:
- 25 June 2020
- Print publication:
- 09 July 2020, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation