Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Approximate evaluation of integrals
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / July 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 110-118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An Euler-Poisson system in plasmas
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 442-450
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Derivative-type ascent formulas for kernels of some half-space Dirichlet problems
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / October 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 185-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On algorithms for generalised smoothing splines
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / January 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 322-341
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Independent non-identical five-parameter gamma-Weibull variates and their sums
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / October 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 265-271
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Minimal approximate Hessians for continuously Gâteaux differentiable functions
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 3 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 349-359
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Initiation of combustion waves in solids, and the effects of geometry
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / July 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 149-163
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On an integral of Lommel and Bessel functions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / April 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 439-444
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The numerical solution of Hammerstein equations by a method based on polynomial collocation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / January 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 319-329
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Some new results for the Lagrange polynomials in several variables
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 2 / October 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 243-258
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The dual reciprocity boundary element method for magnetohydrodynamic channel flows
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / October 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 305-322
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 32 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / October 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critical initial conditions for spatially-distributed thermal explosions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / January 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 350-362
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 46 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 4 / April 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 36 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / April 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A mathematical model and related problems of optimal management and design in a broadband integrated services network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / October 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 150-175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cyclic gravity waves in deep water
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 1 / July 1983
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 2-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the convergence of an iterative method for the minimax problem
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 39 / Issue 2 / October 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 280-292
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 36 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 3 / January 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Existence theorems for Segal quantization via spectral theory in Krein space
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / April 1983
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 439-460
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
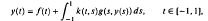
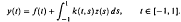
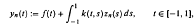
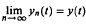 , uniformly in
, uniformly in 