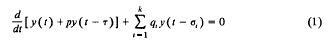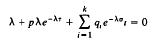Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Necessary and sufficient condition for oscillations of neutral differential equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 3 / January 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 362-375
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The deformation of rubber cylinders and tubes by rotation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / June 1977
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 62-96
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Conservation laws for second-order parabolic partial differential equations
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 3 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 333-348
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On an inequality relating to sum sets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / October 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 208-211
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 46 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / October 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Low Reynolds number flow in a heated tube of varying section
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 2 / October 1983
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 244-260
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The inverse fractional matching problem
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 484-496
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Guide expansions for the recursive parametric solution of polynomial dynamical systems
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / January 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 387-396
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Inertial manifold for a reaction diffusion equation model of competition in a chemostat
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / July 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 9-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Robust guaranteed cost control for descriptor systems with Markov jumping parameters and state delays
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 4 / April 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 569-580
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the dynamic analysis of a Leontief model with fixed capitial
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / April 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 473-487
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The BMAP/G/1 vacation queue with queue-length dependent vacation schedule
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / October 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 207-221
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contents of Volume 25
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / April 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 563-564
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Bifurcation phenomena for an oxidation reaction in a continuously stirred tank reactor. II Diabatic operation
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 3 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 303-326
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Degree reduction of Bezier curves and its error analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / April 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 399-413
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 26 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Subharmonic orbits in an anharmonic oscillator
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 307-315
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Integro-differential equations for the self-organisation of liver zones by competitive exclusion of cell-types
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / October 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 156-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 45 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 36 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / July 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation