Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
ANZ Volume 49 Issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 1 / July 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Continuity properties of attractors for iterated fuzzy set systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 175-193
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 35 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / April 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Critical values for a nonlinear difference equation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 3 / January 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 340-361
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Flow fields associated with in situ mineral leaching
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 133-151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 46 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 3 / January 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Entry flow in a straight circular pipe
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / July 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 59-66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An ordinary differential equation arising in the Ricci flow on the plane
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / January 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 438-444
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Controllability of generalised dynamical systems with constrained control
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / July 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 69-78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The elastodynamic Green's tensor for the 2D half-space
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 4 / December 1978
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 385-400
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Analysis of shallow shells by a combination of finite elements and contour methods
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / April 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 469-491
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Boundary conditions optimal control
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / January 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 343-349
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Laplace transforms for superexponential functions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / July 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 17-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Converging factors for some asymptotic moment series that arise in numerical quadrature
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / October 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 223-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sub-supersolutions in a variational inequality related to a sandpile problem
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / October 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 179-197
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Remarks on the boundary element method for strongly nonlinear problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 419-438
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Speech by Professor G. C. Wake for the Professor B. F. Gray dinner
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / July 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. iv-vi
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On nonlinear programming and matrix game equivalence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / April 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 429-438
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the generalized complementarity problem
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / April 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 420-428
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Strongly nonlinear vortices in magnetized ferrofluids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / October 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 146-170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
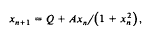
 , where μ
, where μ with
with 