Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
243 results in 65Mxx
Reduced Basis Approaches in Time-Dependent Non-Coercive Settings for Modelling the Movement of Nuclear Reactor Control Rods
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 June 2016, pp. 23-59
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Differential Quadrature Analysis of Moving Load Problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2016, pp. 536-555
- Print publication:
- August 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Osher Flux with Entropy Fix for Two-Dimensional Euler Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2016, pp. 670-692
- Print publication:
- August 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-Order Mesh Generation for Discontinuous Galerkin Methods Based on Elastic Deformation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2016, pp. 693-702
- Print publication:
- August 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spectral-Collocation Method for Volterra Delay Integro-Differential Equations with Weakly Singular Kernels
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2016, pp. 648-669
- Print publication:
- August 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Parameter-Free Time Adaptivity Based on Energy Evolution for the Cahn-Hilliard Equation
- Part of
- Miscellaneous topics - Partial differential equations
- Partial differential equations, initial value and time-dependent initial-boundary value problems
- Elliptic equations and systems
- Partial differential equations, boundary value problems
- Equations of mathematical physics and other areas of application
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1542-1563
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Dimensional Splitting of ETD Schemes for Reaction-Diffusion Systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1343-1356
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Adaptive Time Stepping Method for Transient Dynamic Response Analysis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- East Asian Journal on Applied Mathematics / Volume 6 / Issue 2 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2016, pp. 152-170
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Fully Decoupled, Convergent Schemes for Diffuse Interface Models for Two-Phase Flow with General Mass Densities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1473-1502
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accurate and Efficient Numerical Methods for Computing Ground States and Dynamics of Dipolar Bose-Einstein Condensates via the Nonuniform FFT
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1141-1166
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Full Space-Time Convergence Order Analysis of Operator Splittings for Linear Dissipative Evolution Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1302-1316
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Entropy Stable Scheme on Two-Dimensional Unstructured Grids for Euler Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1111-1140
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Two-Grid Method for Miscible Displacement Problem by Mixed Finite Element Methods and Mixed Finite Element Method of Characteristics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1503-1528
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Solving Maxwell's Equation in Meta-Materials by a CG-DG Method
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1242-1264
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Priori Error Estimate of Splitting Positive Definite Mixed Finite Element Method for Parabolic Optimal Control Problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Numerical Mathematics: Theory, Methods and Applications / Volume 9 / Issue 2 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2016, pp. 215-238
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Novel Symplectic Discrete Singular Convolution Method for Hamiltonian PDEs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1375-1396
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Anisotropic Convection-Diffusion Model Using Tailored Finite Point Method for Image Denoising and Compression
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1357-1374
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chebyshev-Legendre Spectral Domain Decomposition Method for Two-Dimensional Vorticity Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2016, pp. 1221-1241
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Invariant-Preserving Finite Difference Schemes for the Camassa-Holm Equation and the Two-Component Camassa-Holm System
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2016, pp. 1015-1041
- Print publication:
- April 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Divergence-Free WENO Reconstruction-Based Finite Volume Scheme for Solving Ideal MHD Equations on Triangular Meshes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2016, pp. 841-880
- Print publication:
- April 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
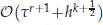 are obtained when polynomials of degree at most
are obtained when polynomials of degree at most 