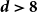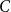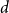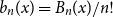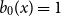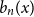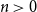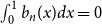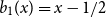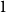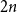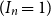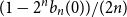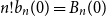Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52629 results in Statistics and Probability
Tables
-
- Book:
- Applying Benford's Law for Assessing the Validity of Social Science Data
- Published online:
- 09 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 1 - Introduction
-
- Book:
- Applying Benford's Law for Assessing the Validity of Social Science Data
- Published online:
- 09 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp 1-10
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Applying Benford's Law for Assessing the Validity of Social Science Data
- Published online:
- 09 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 2 - Validity and Self-Reported Data
-
- Book:
- Applying Benford's Law for Assessing the Validity of Social Science Data
- Published online:
- 09 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp 11-23
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 8 - Conclusion
-
- Book:
- Applying Benford's Law for Assessing the Validity of Social Science Data
- Published online:
- 09 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp 188-195
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Spread-out limit of the critical points for lattice trees and lattice animals in dimensions
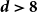 $\boldsymbol{d}\boldsymbol\gt \textbf{8}$
$\boldsymbol{d}\boldsymbol\gt \textbf{8}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 238-269
-
- Article
- Export citation
SUBGEOMETRICALLY ERGODIC AUTOREGRESSIONS WITH AUTOREGRESSIVE CONDITIONAL HETEROSKEDASTICITY
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 41 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 218-248
-
- Article
- Export citation
A comparative analysis of public transport accessibility to hospitals in Córdoba (2019–2023): Where are we now?
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimal performance of a tontine overlay subject to withdrawal constraints
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 94-128
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp i-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
References
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 506-523
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Interactions and Unordered Dependent Variables
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 433-492
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Figures
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp xiii-xvii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix A - Basic Properties of Variances
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 493-494
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Tables
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp xviii-xx
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Introduction
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 1-12
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix D - Calculating the Values of the Modifying Variable Z at which the Bounds of the Confidence Interval for the Marginal Effect of X Equal 0
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 500-505
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Solutions
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 524-577
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Bernoulli clock: probabilistic and combinatorial interpretations of the Bernoulli polynomials by circular convolution
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 210-237
-
- Article
- Export citation
Appendix B - Marginal Effects and Variances for Various Linear-Interactive Models
-
- Book:
- Interaction Models
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2023, pp 495-497
-
- Chapter
- Export citation