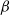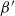Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52651 results in Statistics and Probability
A mapping method for anomaly detection in a localized population of structures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2022, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bounds for the chi-square approximation of the power divergence family of statistics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2022, pp. 1059-1080
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A probabilistic model for interfaces in a martensitic phase transition
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2022, pp. 1081-1105
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A unifying approach to non-minimal quasi-stationary distributions for one-dimensional diffusions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2022, pp. 1106-1128
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Building better global data governance
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 4 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2022, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Construction of aggregation paradoxes through load-sharing models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2022, pp. 223-244
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Serial interval in households infected with SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.529 (Omicron) is even shorter compared to Delta
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2022, e165
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Burkholderia cepacia complex outbreak linked to a no-rinse cleansing foam product, United States – 2017–2018
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2022, e154
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Scaling limits of branching random walks and branching-stable processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2022, pp. 1009-1025
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation

Large Deviations for Markov Chains
-
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022
CONSISTENT LOCAL SPECTRUM INFERENCE FOR PREDICTIVE RETURN REGRESSIONS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 38 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, pp. 1253-1307
-
- Article
- Export citation
SIMULTANEOUS CONFIDENCE BANDS FOR CONDITIONAL VALUE-AT-RISK AND EXPECTED SHORTFALL
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, pp. 1009-1043
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
PES volume 36 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The changing roles of frontline bureaucrats in the digital welfare state: The case of a data dashboard in Rotterdam’s Work and Income department
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 4 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PES volume 36 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Unbiased estimator for the ultimate claim prediction error in the chain-ladder model of Mack
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Actuarial Science / Volume 17 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 118-144
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The
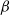 $\beta$-Delaunay tessellation: Description of the model and geometry of typical cells
$\beta$-Delaunay tessellation: Description of the model and geometry of typical cells
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 1252-1290
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interacting nonlinear reinforced stochastic processes: Synchronization or non-synchronization
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 275-320
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bonus-Malus Scale models: creating artificial past claims history
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Actuarial Science / Volume 17 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2022, pp. 36-62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk of acquiring Ascaris lumbricoides infection in an endemically infected rural community in Venezuela
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2022, e151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation