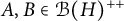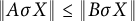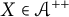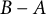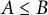Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418807 results in Open Access
Every symmetric Kubo–Ando connection has the order-determining property
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 279-288
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Order continuity of Arens extensions of regular multilinear operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 258-279
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Synergy of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for Enhanced Disaster Management: Opportunities and Challenges
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, e507
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Photon-shielding properties of alkali- and acid-treated Philippine natural zeolite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 258-266
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hypoxia following warden procedure: evaluation and percutaneous treatment
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 634-636
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of dietary and lifestyle inflammation score with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiometabolic risk factors in Iranian adults: Sabzevar Persian Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 521-530
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between urinary potassium excretion, serum potassium levels and cardiac injury in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease: KoreaN cohort study for Outcome in patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD)
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 429-437
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A New Experience in the Turkish Health System in Response to COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, e483
-
- Article
- Export citation
When Are Norms Prescriptive? Understanding and Clarifying the Role of Norms in Behavioral Ethics Research
-
- Journal:
- Business Ethics Quarterly / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 331-364
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unfulfilled Promises and Desires: The British South Africa Company (BSAC), Settler Politics and the Development of Southern Rhodesia’s Fiscal System, 1890–1922
-
- Journal:
- Enterprise & Society / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 1025-1048
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Law as an Instrument: Sources of Chinese Law for Authoritarian Legality by Shucheng Wang. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. 310 pp. Hardcover: US$ 110.00
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Comparative Law / Volume 18 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 446-448
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the reproductive strategies post-colony foundation: major termite pest species with distinct ecological habits differ in their oviposition dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 716-724
-
- Article
- Export citation
JAZ volume 115 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 115 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Standardization of the Emergency Department Response to Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear (CBRN) Events: Human Factors/Ergonomics Approach
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, e487
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ROBERT TRIFFIN, JAPAN, AND THE QUEST FOR ASIAN MONETARY UNION
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 92-116
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Negative-pressure rooms and Aspergillus risk—Air balance alone is insufficient
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 2096-2097
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conditional Freedoms: Non-State Labour in Cuba between Institutional Delegitimisation and Civic Recognition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Latin American Studies / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 599-622
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Susanne Flach and Martin Hilpert (eds.), Broadening the spectrum of corpus linguistics: New approaches to variability and change (Studies in Corpus Linguistics 105). Amsterdam and Philadelphia: John Benjamins, 2022. Pp. vi + 321. ISBN 9789027212665.
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 439-445
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dairy products and brain structure in French older adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 512-520
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation