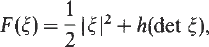Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25816 results in Abstract analysis
PRM volume 127 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Oscillation theory for indefinite Sturm-Liouville problems with eigenparameter-dependent boundary conditions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 6 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1123-1136
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
A variational approach to multiplicity in elliptic problems near resonance*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 385-394
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
On rank-one convex and polyconvex conformal energy functions with slow growth
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 3 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 651-663
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homogenisation and θ — 2 convergence
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 3 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 441-455
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Regularity of the solutions for elliptic problems on nonsmooth domains in ℝ3. Part II: Regularity in neighbourhoods of edges
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 3 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 517-545
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Normal curvature of minimal submanifolds in a sphere
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 29-33
- Print publication:
- January 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Convergence of the viscosity solutions for weakly strictly hyperbolic conservation laws*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1103-1110
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Regularity results for equilibria in a variational model for fracture
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 889-902
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
The KO-cohomology ring of SU (2n)/SO (2 n)
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 91-97
- Print publication:
- January 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Some new properties of Sobolev mappings: intersection theoretical approach
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 337-358
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
A perturbation result of semilinear elliptic equations in exterior strip domains
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 983-1004
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Travelling wave solutions for a balance law
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 3 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 567-593
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
The spectrum and eigenspaces of a meromorphic operator-valued function
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1027-1051
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Positive solution curves of semipositone problems with concave nonlinearities*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 921-934
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spectral properties of the Orr-Sommerfeld problem
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 6 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1245-1261
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 127 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A combinatorial procedure for finding isolating neighbourhoods and index pairs
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1075-1088
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Positive solutions for the p-Laplacian: application of the fibrering method
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 4 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 703-726
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Commutative 2-local ring spectra
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1-10
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
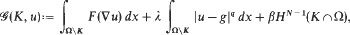
 corresponding to polyconvex bulk energy densities of the form
corresponding to polyconvex bulk energy densities of the form