Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25816 results in Abstract analysis
Jacobi elliptic algebras of SO(3)
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 115-120
- Print publication:
- January 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Diffusion-mediated permanence problem for a heterogeneous Lotka–Volterra competition model
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 281-336
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equations with an infinite number of explicit conservation laws
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 11-19
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Extensions of semilattices by left type-A semigroups
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 7-16
- Print publication:
- January 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Regularity of plate equations with control concentrated in interior curves
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1005-1025
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Global smooth solutions for a class of quasilinear hyperbolic systems with dissipative terms
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 6 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1311-1324
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pattern formation of the stationary Cahn-Hilliard model
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 6 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1219-1243
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of affine ruled surfaces
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 17-20
- Print publication:
- January 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On gradients of approximate travelling waves for generalised KPP equations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 423-439
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Semigroup identities on units of integral group rings
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2009, pp. 1-6
- Print publication:
- January 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Boundary value problems for elliptic pseudodifferential operators II
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 395-405
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compactness and single-point blowup of positive solutions on bounded domains
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 47-65
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
The viscous damping prevents propagation of singularities in the system of viscoelasticity
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1067-1074
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of mixed boundary conditions in some reaction–diffusion systems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 1053-1066
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotic behaviour of the solutions of the supercooled Stefan problem
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 181-189
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 127 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Boundedness of operators of Hardy type in ΛP,q spaces and weighted mixed inequalities for singular integral operators*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 157-170
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Remarks on spherically symmetric solutions of the compressible Euler equations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 243-259
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stability and instability of steady-state solutions for a hydrodynamic model of semiconductors
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 4 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 781-796
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
Singular boundary value problems for P-Laplacian-like equations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2011, pp. 975-981
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
- Export citation
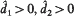 such that for every
such that for every 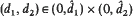 the RD-model is
the RD-model is 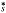 , be defined by
, be defined by 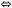 [(
[(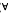
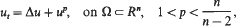
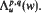 These spaces were introduced by M. J. Carro and J. Soria and include weighted
These spaces were introduced by M. J. Carro and J. Soria and include weighted 