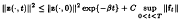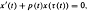Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Love's integral and other relations between solutions to mixed boundary-value problems in potential theory
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / January 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 353-367
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Strong uniqueness in sequential linear programming
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 4 / April 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 379-384
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 36 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / July 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 31 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / January 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Extreme stability and almost periodicity in continuous and discrete neuronal models with finite delays
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / October 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 261-282
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 20 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / June 1978
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Static plane-symmetric solution of a scalar-tensor theory of gravitation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / January 1983
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 339-342
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Initial value formalism for Lemaitre-Tolman-Bondi collapse
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 1 / July 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 53-73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Usage of the convergence test of the residual norm in the Tsuno-Nodera version of the GMRES algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 2 / October 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 293-308
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Averaging of the Hamilton-Jacobi equation in infinite dimensions and an application
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 41 / Issue 3 / January 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 372-385
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Numerical algorithms for constrained maximum likelihood estimation
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / July 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 91-114
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An algorithm for solving the restricted least squares problem
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / January 1980
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 345-356
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Pointwise estimates for higher order convexity preserving polynomial approximation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 213-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A note on the boundary integral equation method for the solutions of second order elliptic equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 415-421
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Some remarks on a quasi-steady-state approximation of the Navier-Stokes equation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / April 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 440-447
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On error bounds in strong approximations for eigenvalue problems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / January 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 270-283
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Oscillation of first-order delay differential equations
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 593-599
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ Volume 49 Issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 1 / July 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Inverse coefficient problems for nonlinear elliptic equations
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 2 / October 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 271-279
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 21 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / August 1979
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation