Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Efficiency and generalised convexity in vector optimisation problems
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 523-546
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Numerical solution of an evolution equation with a positive-type memory term
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 1 / July 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 23-70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A programming problem with an Lp norm in the objective function
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 3 / June 1976
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 333-342
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 47 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 1 / July 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The anti-cyclonic shear wave: a new geophysical wave
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 1 / July 1983
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 110-126
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Singular problems modelling phenomena in the theory of pseudoplastic fluids
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / October 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 167-179
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contents of Volume 27
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / April 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 512-513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Rank-1 perturbations and the Lanczos method, inverse iteration, and Krylov subspaces
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / April 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 381-388
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Inverse power law potentials about polygonal prisms and in polygonal cavities
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / December 1977
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 241-253
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A certain class of generating functions involving bilateral series
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 3 / January 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 475-483
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Explicit bounds for third-order difference equations
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / January 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 359-366
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dynamics of a delayed population model with feedback control
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 451-457
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 19 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / December 1976
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A three-dimensional numerical model of the response of the Australian North West Shelf to tropical cyclones
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / July 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 64-100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Collocation methods for two dimensional weakly singular integral equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 22 / Issue 4 / April 1981
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 456-473
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 39 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 39 / Issue 2 / October 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A C0-Collocation-like method for elliptic equations on rectangular regions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / January 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 368-387
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Concise representation of generalised gradients
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / July 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 57-74
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Infinitely divisible random transition probabilities with application to dependent Markov chains
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / April 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 463-472
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 41 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
 . Here ρ
. Here ρ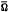 ⊆
⊆ 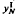 and
and 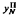 , two different numerical approximations to its solution, using the collocation and iterated collocation methods respectively. We describe without proof some known results concerning the general convergence properties of
, two different numerical approximations to its solution, using the collocation and iterated collocation methods respectively. We describe without proof some known results concerning the general convergence properties of 