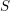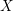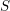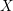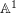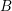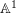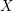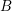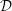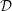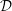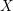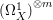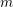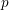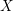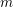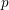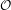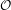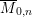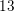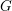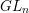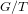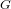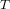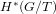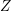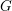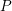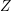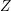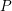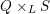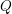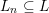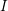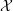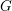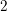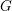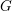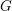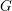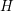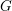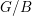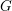Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
200 results in 14Mxx
Local models for Weil-restricted groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 12 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2016, pp. 2563-2601
- Print publication:
- December 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
FAMILIES OF AFFINE RULED SURFACES: EXISTENCE OF CYLINDERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 223 / Issue 1 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2016, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SUPERORBITS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 17 / Issue 5 / November 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2016, pp. 1065-1120
- Print publication:
- November 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characters of equivariant
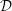 ${\mathcal{D}}$ -modules on spaces of matrices
${\mathcal{D}}$ -modules on spaces of matrices
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 9 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2016, pp. 1935-1965
- Print publication:
- September 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
SINGULAR RATIONALLY CONNECTED THREEFOLDS WITH NON-ZERO PLURI-FORMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 221 / Issue 1 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2016, pp. 3-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the equations and classification of toric quiver varieties
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 146 / Issue 2 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2016, pp. 265-295
- Print publication:
- April 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homaloidal nets and ideals of fat points I
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- LMS Journal of Computation and Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2016, pp. 54-77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PERVERSE MOTIVES AND GRADED DERIVED CATEGORY
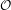 ${\mathcal{O}}$
${\mathcal{O}}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 17 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2016, pp. 347-395
- Print publication:
- April 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Some non-finitely generated Cox rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2015, pp. 984-996
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compactifications of reductive groups as moduli stacks of bundles
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 1 / January 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2015, pp. 62-98
- Print publication:
- January 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Schubert presentation of the cohomology ring of flag manifolds
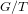 $G/T$
$G/T$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- LMS Journal of Computation and Mathematics / Volume 18 / Issue 1 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2015, pp. 489-506
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
COX RINGS OF MINIMAL RESOLUTIONS OF SURFACE QUOTIENT SINGULARITIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2015, pp. 325-355
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PARTIALLY AMPLE LINE BUNDLES ON TORIC VARIETIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2015, pp. 587-598
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The local structure theorem for real spherical varieties
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 11 / November 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2015, pp. 2145-2159
- Print publication:
- November 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hilbert series of residual intersections
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 9 / September 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2015, pp. 1663-1687
- Print publication:
- September 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
A mirror theorem for toric stacks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 10 / October 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2015, pp. 1878-1912
- Print publication:
- October 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Invariants of degree 3 and torsion in the Chow group of a versal flag
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 8 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2015, pp. 1416-1432
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the derived category of Grassmannians in arbitrary characteristic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 7 / July 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2015, pp. 1242-1264
- Print publication:
- July 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Log Canonical Thresholds of Complete Intersection Log Del Pezzo Surfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2015, pp. 445-483
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Spherical subgroups in simple algebraic groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 151 / Issue 7 / July 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2015, pp. 1288-1308
- Print publication:
- July 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation