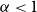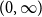Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52666 results in Statistics and Probability
ECT volume 37 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Characterization of Philippine natural bentonite
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON COMPLEX ECONOMIC SCENARIO GENERATORS: IS LESS MORE?
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2021, pp. 779-812
- Print publication:
- September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The distance profile of rooted and unrooted simply generated trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2021, pp. 368-410
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A closed-form approximation formula for pricing European options under a three-factor model
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2021, pp. 1214-1240
-
- Article
- Export citation
Game theoretic modeling of economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) attack in cloud computing
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2021, pp. 1241-1265
-
- Article
- Export citation
SARS-CoV-2 immunogenicity in individuals infected before and after COVID-19 vaccination: Israel, January–March 2021
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2021, e239
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysing the reported incidence of COVID-19 and factors associated in the World Health Organization African region as of 31 December 2020
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2021, e256
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
UNIFORM INFERENCE IN A GENERALIZED INTERVAL ARITHMETIC CENTER AND RANGE LINEAR MODEL
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. 27-69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
THE INFORMATION BOUND OF A DYNAMIC PANEL LOGIT MODEL WITH FIXED EFFECTS — CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, p. 219
-
- Article
- Export citation
COMPLETE SUBSET AVERAGING FOR QUANTILE REGRESSIONS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. 146-188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
On the correction of temperatures derived from meteor wind radars due to geomagnetic activity
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2021, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
University students and staff able to maintain low daily contact numbers during various COVID-19 guideline periods
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e169
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence survey among health care providers in a Belgian public multiple-site hospital
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e172
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Adenovirus pneumonia should not be overlooked in immunocompetent youths and adults
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Changes in COVID-19-related outcomes, potential risk factors and disparities over time
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e192
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vitamin D levels in children with COVID-19: a report from Turkey
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e180
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serological and molecular detection of pathogenic Leptospira in domestic and stray cats on Reunion Island, French Indies
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e229
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Toxigenic Clostridium difficile-mediated diarrhoea in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in-patients: rapid diagnosis and efficient treatment
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e250
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiological investigations identified an outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serotype O26:H11 associated with pre-packed sandwiches
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e178
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation