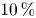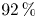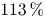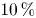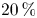Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418034 results in Open Access
Lenore A. Grenoble & Jessica Kantarovich, Reconstructing non-standard languages: A socially-anchored approach. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, 2022. Pp. xv, 354. Hb. €100.
-
- Journal:
- Language in Society / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, pp. 173-174
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Abolitionist Decrees in Ethiopia: The Evolution of Anti-Slavery Legal Strategies from Menilek to Haile Selassie, 1889–1942
-
- Journal:
- Law and History Review / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 97-117
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
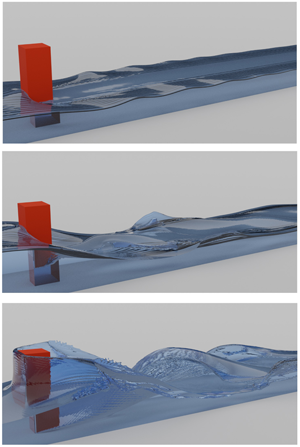
Free-surface channel flow around a square cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, A16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Abolition of Slavery in Africa's Legal Histories
-
- Journal:
- Law and History Review / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2024, pp. 1-29
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rainbow Serpents and Boiling Springs: Indigenous Sovereignty and the Fight for Groundwater in the United States and Australia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of American Studies / Volume 58 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, pp. 1-38
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Whey protein concentrate and skimmed milk powder as encapsulation agents for coffee silverskin extracts processed by spray drying
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 91 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, pp. 96-98
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Between race and animality: European borders, ‘colonial dogs’, and the policing of humanity
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Agreement Under the U.N. Convention on the Law of the Sea on the Conservation & Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction
-
- Journal:
- International Legal Materials / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, pp. 1-46
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ralph Rodríguez, Latinx Literature Unbound: Undoing Ethnic Expectation (New York: Fordham University Press, 2018, $32.99). Pp. 200. isbn 978 0 8232 7924 1. - José Esteban Muñoz, The Sense of Brown (Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2020, $26.95). Pp. 224. isbn 978 1 4780 1103 3.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of American Studies / Volume 58 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, pp. 150-153
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Managing Uncertain Times in Turkey: Refugee Healthcare Research during a Global Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Middle East Studies / Volume 56 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 151-156
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JLI volume 52 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Legal Information / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / Summer 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2025, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- Summer 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Egyptian Fan Culture and the Afterlife of ʿAbd al-Halim Hafiz
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Middle East Studies / Volume 56 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, pp. 1-17
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measures of Justice: A Symposium in Honor of Sally Engle Merry (1944–2020)
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry / Volume 49 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, pp. 1-6
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Functional properties of cream and butter oil from milk of Holstein cows abomasally infused with increasing amounts of high-oleic sunflower fatty acids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 91 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, pp. 10-18
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Future Is History: Restorative Nationalism and Conflict in Post-Napoleonic Europe
-
- Journal:
- International Organization / Volume 78 / Issue 2 / Spring 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2024, pp. 259-292
- Print publication:
- Spring 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Community and Conflict in the Chronicle of Bury St Edmunds
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 75 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, pp. 231-249
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Surface gravity wave-induced drift of floating objects in the diffraction regime
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, A27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rise and Fall of Imperial China: The Social Origins of State Development By Yuhua Wang. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2022. 322 pp. $120.00 (cloth), $35.00 (paper)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Chinese History / Volume 8 / Issue 2 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, pp. 432-440
-
- Article
- Export citation