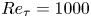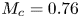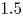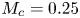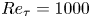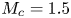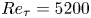Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417865 results in Open Access
Bladelets, Blood, and Bones: Integrating Protein Residue, Lithic Use-Wear, and Faunal Data from the Moorehead Circle, Fort Ancient – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, p. 340
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The lack of agency becoming part of the self
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Advances / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 166-167
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lori Jones (ed.), Disease and the Environment in the Medieval and Early Modern Worlds (London and New York: Routledge, 2022). ISBN 9780367151720. Pages 230 + figures 9, £26.24 paperback and Ebook, £97.50 hardback.
-
- Journal:
- Continuity and Change / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 129-131
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
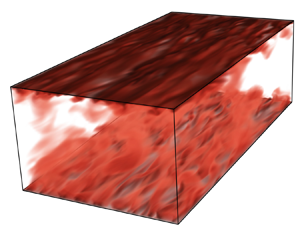
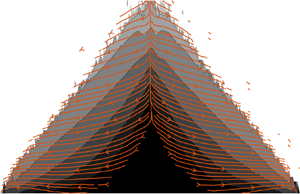
A wall model for large-eddy simulation of highly compressible flows based on a new scaling of the law of the wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Naturalistic assessment of reaction time variability in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 428-438
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of early postoperative haemodynamic and laboratory parameters on outcome after the Fontan procedure
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 1304-1311
-
- Article
- Export citation
Psychological factors in symptom severity and quality of life in Raynaud’s phenomenon
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 52 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 426-439
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Type material of Paraconularia planicostata (Dawson) from the Upper Mississippian of Nova Scotia, Atlantic Canada
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 98 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 152-155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The stress in static granular media under gravity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Which training leads to employment? The effectiveness of varying types of training programmes for unemployed jobseekers in Flanders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Social Policy / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 651-672
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maternal cognitive functioning and psychopathology predict quality of parent-child relationship in the context of substance use disorder: A 15-month longitudinal study
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 439-450
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rare cardiac tumour-nodular fasciitis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 933-934
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factor Model Comparisons with Conditioning Information
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 60 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 1401-1426
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Amanda Lanzillo, Pious Labour: Islam, Artisanship, and Technology in Colonial India Berkeley: University of California Press, 2024. Pp. 246. ISBN 978-0-520-39857-3. £30.00 (paperback).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 301-303
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Development of robust normative data for the neuropsychological assessment of Greek older adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 6 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 594-602
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Premorbid personality traits as predictors for incident predementia syndromes: a multistate model approach
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 6 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 564-574
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MAXIMAL SUBSEMIGROUPS OF INFINITE SYMMETRIC GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 324-337
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation