Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417448 results in Open Access
JWST imaging observations of the Ring Nebula
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S384 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2025, pp. 183-189
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
NEW LIGHT IN CHRISTODORUS: AN ACROSTIC AT ANTH. PAL. 2.72–6
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 73 / Issue 2 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2024, pp. 965-969
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CQY volume 256 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 256 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ordered Groups, Computability and Cantor-Bendixson Rank
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Symbolic Logic / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, p. 664
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Images of Miraculous Healing in the Early Modern Netherlands. Barbara A. Kaminska. Brill's Studies on Art, Art History, and Intellectual History 58. Leiden: Brill, 2022. xvi + 268 pp. $167.
-
- Journal:
- Renaissance Quarterly / Volume 76 / Issue 4 / Winter 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2024, pp. 1483-1485
- Print publication:
- Winter 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Complexity of emerging magnetic flux during lifetime of solar ephemeral regions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S365 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2024, pp. 303-310
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Flux emergence simulation and coronal response at ephemeral region scale
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S365 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2024, pp. 340-344
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Aftersun, directed by Charlotte Wells (2022) – Psychiatry in movies
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, p. 554
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ENG volume 39 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- English Today / Volume 39 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2024, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Democracy amid Crises: Polarization, Pandemic, Protests, and Persuasion. Edited by the Annenberg IOD Collaborative: Matthew Levendusky, Josh Pasek, Bruce Hardy, R. Lance Holbert, Kate Kenski, Yotam Ophir, Andrew Renninger, Daniel Romer, Dror Walter, Ken Winneg, and Kathleen Hall Jamieson. New York: Oxford University Press, 2023. 484p. $99.00 cloth, $24.95 paper.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2023, pp. 1468-1469
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
D. D. Dzhafarov and C. Mummert, Reverse Mathematics: Problems, Reductions, and Proofs. Theory and Applications of Computability. Springer Nature, Cham, 2022, xix + 488 pp.
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Symbolic Logic / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 660-662
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
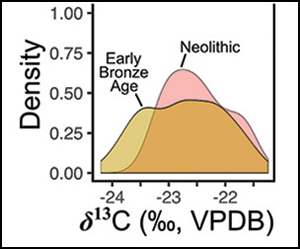
Changing human-cattle relationships in Ireland: a 6000-year isotopic perspective
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Finding Order in Diversity: Religious Toleration in the Habsburg Empire, 1792–1848 By Scott Berg. West Lafayette, Indiana: Purdue University Press, 2022. Pp. xviii + 344. Paperback $59.99. ISBN: 978-1612496962.
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2023, pp. 623-624
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Configuring Cultural Emerging Industries: A Comparison of the French and Italian Fashion Industries
-
- Journal:
- Business History Review / Volume 97 / Issue 4 / Winter 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2024, pp. 779-807
- Print publication:
- Winter 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
APR volume 55 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 December 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Beneath the surface, below the line: Exploring household differentiation at Las Cuevas using Gini coefficients
-
- Journal:
- Ancient Mesoamerica / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / Fall 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2024, e10
- Print publication:
- Fall 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Everyone can make mistakes, but not everyone can fail: a response to Price & Jaffe
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is ChatGPT Any Good at Legal Research – and Should We be Wary or Supportive of it?
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 219-224
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the predictability of the solar cycle from the polar field rise rate: Results from observations and simulations
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S365 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2024, pp. 148-153
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
ASO volume 43 issue 12 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation