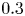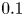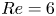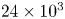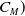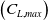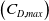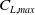Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418788 results in Open Access
Stochastic particle transport by deep-water irregular breaking waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, A38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Applying geostatistical hotspot analyses to a ‘double-invaded’ plant–pest co-occurrence scenario
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 241-250
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A length scale for non-local multi-scale gradient interactions in isotropic turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, A40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What’s in the mind’s eye of individuals with bipolar disorders: an exploration of the content and characteristics of mental images in different thymic phases
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 178-193
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Process of Revolutionary Protest: Development and Democracy in the Tunisian Revolution
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 103-121
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of diets containing fish oils or fish oil concentrates with high cetoleic acid content on the circulating cholesterol concentration in rodents. A systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 606-621
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A systematic investigation into the effect of roughness on self-propelled swimming plates
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, A39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Federalism for Bioethics?
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 112-120
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Synthesizing Methuselah: The Question of Artificial Agelessness
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 60-75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Older Men, The Patient–Physician Relationship, and Patient Involvement
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 142-152
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Increasing fibre intake in the UK: lessons from the Danish Whole Grain Partnership
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 672-685
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clean hospitals day 2023 marks the global launch of a self-assessment tool
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, p. 1704
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social Protection under Authoritarianism: Health Politics and Policy in China Xian Huang. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2020. 272 pp. £26.49 (pbk). ISBN 9780197642771
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 256 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 1112-1114
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mental health in society’s margins: poor n-3 PUFA intake and psychological well-being of homeless youth
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 698-706
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical investigation of the dynamic stall reduction on the UAS-S45 aerofoil using the optimised aerofoil method
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1321 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 441-468
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Woman between Us: Sarah Nakimu Nalwanga and the Founding of Uganda’s Anglican Tradition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 95-108
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Finite Froude and Rossby numbers counter-rotating vortex pairs
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, A41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Joseph C. Schmid and Daniel J. Linford, Existential Inertia and Classical Theistic Proofs (Cham: Springer, 2023). Pp. xvi + 378. £104.25. (Hbk). ISBN 9783031193125.
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies / Volume 61 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 258-262
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Instability of the optimal edge trajectory in the Blasius boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, A42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation