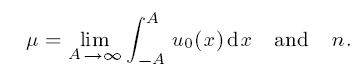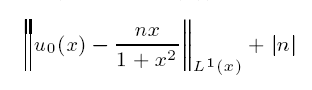Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25843 results in Abstract analysis
Large-time behaviour of solutions of Burgers' equation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 4 / August 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 843-878
- Print publication:
- August 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
On convergence, admissibility and attractors for damped wave equations on squeezed domains
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 4 / August 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 765-791
- Print publication:
- August 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Singular limit of reactiondiffusion systems and modified motion by mean curvature
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 132 / Issue 4 / August 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 951-973
- Print publication:
- August 2002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genus spectra for split metacyclic groups
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 209-218
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prime numbers of the form [nc]
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 237-254
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Gabriel topologies on Dubrovin valuation rings
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 317-325
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Splitting off free summands of torsion-free modules over complete DVRs
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 349-351
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
One parameter families of Riemann surfaces of genus two
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 255-268
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the Chordal Transform of Hilbert Space Operators
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 275-284
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Class of Exponent-Sum Two Equations Over Groups
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 201-207
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Distributed control of a heat conducting, time-dependent, Navier-Stokes fluid
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 191-200
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The N-soliton solution of a generalised Vakhnenko equation
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue A / June 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 65-90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Semiperfect rings and Nakayama permutations
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 301-309
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Carleson measures theorems for generalized Bergman spaces on the unit polydisk
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 277-294
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dichotomies of solutions for a class of second-order nonlinear differential equations
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 339-348
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Extremal Algebra on Two Hermitians With Square 1
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 255-260
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Extremal Kähler metrics and Hamiltonian functions II
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 241-253
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On q-hyperelliptic k-bordered tori
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 343-357
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Normed units in abelian group rings
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 365-373
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dimensions of quantum determinantal rings
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2002, pp. 285-292
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation