Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6994 results in Mathematical modeling and methods
Nonlinear free-surface flows emerging from vessels and flows under a sluice gate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / July 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 63-86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contact problem of an elastic plug in an elastic region
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 2 / December 1975
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 229-241
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of an axisymmetric rigid punch on a nonhomogeneous transversely isotropic half-space
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 44 / Issue 3 / January 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 461-474
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nonlinear oscillations and buckling of anisotropic cylindrical shells under large initial stresses
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / January 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 330-346
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Moving boundary problems in the flow of liquid through porous media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / October 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 171-193
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On a direct method for the determination of an exact invariant for the time-dependent harmonic oscillator
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / June 1977
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 97-105
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Existence of solutions of a class of stochastic Volterra integral equations with applications to chemotherapy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 41 / Issue 1 / July 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 93-104
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On some switching inequalities of Brenner and Alzer
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / October 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 285-288
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Early quasi-steady electro-magnetic fields about conducting surfaces
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 42 / Issue 4 / April 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 481-493
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 25 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / April 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, p. b1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Gradient algorithms for principal component analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / April 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 430-450
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nonnegative solutions for a heterogeneous degenerate competition model
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / October 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 273-297
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 38 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 38 / Issue 4 / April 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An evolutionary monotone follower problem in [0, 1]
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / July 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 97-107
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The structure of solutions for equations related to the motions of plane curves
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 585-592
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Monotonicity of the error term in Gauss-Turán quadratures for analytic function
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 48 / Issue 4 / April 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 567-581
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Isospectral flows and linear programming
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 495-510
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Summing a common type of slowly convergent series of positive terms
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / December 1976
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 416-421
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANZ volume 23 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / April 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Derivatives of addition theorems for Legendre functions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / October 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2009, pp. 212-234
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
 . The method used is that of linear canonical transformations with time-dependent coeffcients. This is a new approach to the problem and has the advantage of simplicity. When
. The method used is that of linear canonical transformations with time-dependent coeffcients. This is a new approach to the problem and has the advantage of simplicity. When 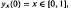 , solutions of
, solutions of 