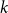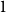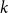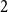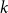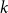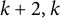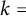Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1073 results in 05Cxx
Satisfiability thresholds for regular occupation problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2025, pp. 491-527
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Right-angled Artin groups and the cohomology basis graph
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2025, pp. 634-654
-
- Article
- Export citation
On perfect subdivision tilings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 January 2025, pp. 421-444
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hypergraph independence polynomials with a zero close to the origin
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2025, pp. 486-490
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rigidity of symmetric simplicial complexes and the lower bound theorem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 13 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2025, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On several dynamical properties of shifts acting on directed trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 78 / Issue 2 / April 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, pp. 375-404
- Print publication:
- April 2026
-
- Article
- Export citation
Restricted sumsets in multiplicative subgroups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 78 / Issue 2 / April 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2025, pp. 594-618
- Print publication:
- April 2026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the (
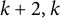 $k + \text{2}, k$)-problem of Brown, Erdős, and Sós for
$k + \text{2}, k$)-problem of Brown, Erdős, and Sós for 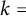 $k =$ 5,6,7
$k =$ 5,6,7
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2025, pp. 1-43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Minimum non-chromatic-choosable graphs with given chromatic number
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2024, pp. 1-32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural convergence and algebraic roots
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2024, pp. 392-400
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vines and MAT-labeled graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, e128
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A SUFFICIENT CONDITION FOR PANCYCLIC GRAPHS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 2 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 220-226
- Print publication:
- October 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tree universality in positional games
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2024, pp. 338-358
-
- Article
- Export citation
Twin-width of sparse random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2024, pp. 401-420
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tight bound for the Erdős–Pósa property of tree minors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2024, pp. 321-325
-
- Article
- Export citation
The power of many colours
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2024, e118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Average distance in a general class of scale-free networks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 371-406
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Continuum limit for interacting systems on adaptive networks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ramsey simplicity of random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2024, pp. 298-320
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON NEIGHBOURHOODS IN THE ENHANCED POWER GRAPH ASSOCIATED WITH A FINITE GROUP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 1 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2024, pp. 149-154
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation