Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1838 results in 60Gxx
H = λG and the Palm transformation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 755-758
- Print publication:
- September 1992
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Work-modulated queues with applications to storage processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 699-712
- Print publication:
- September 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dependence structure of Poisson-paced records
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 587-596
- Print publication:
- September 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the volume distribution of the typical Poisson–Delaunay cell
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 740-744
- Print publication:
- September 1992
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A bang-bang strategy for a finite fuel stochastic control problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 589-603
- Print publication:
- September 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
A note on the multitype measure branching process
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 496-498
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The abscissa of convergence of the Laplace transform
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 353-362
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the system queue length distributions of LCFS-P queues with arbitrary acceptance and restarting policies
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 430-440
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
On strict stationarity and ergodicity of a non-linear ARMA model
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 363-373
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Limit theorems for suprema, threshold-stopped random variables and last exits of i.i.d. random variables with costs and discounting, with applications to optimal stopping
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 241-266
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Applications of the key renewal theorem: crudely regenerative processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 384-395
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Event and time averages: a review
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 377-411
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
On some first-crossing-time probabilities for a two-dimensional random walk with correlated components
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 441-454
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
The maximum and mean of a random length sequence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 460-466
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
A simple proof of Pitman's 2M–X theorem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 499-501
- Print publication:
- June 1992
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Equivalence of two descriptions of the ages of alleles
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / March 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 185-189
- Print publication:
- March 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
The extremal index for a Markov chain
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / March 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 37-45
- Print publication:
- March 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Concavity and reflected Lévy processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / March 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 209-215
- Print publication:
- March 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
A note on one-dimensional chaotic maps under time reversal
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / March 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 219-220
- Print publication:
- March 1992
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Light traffic approximations in many-server queues
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 24 / Issue 1 / March 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 202-218
- Print publication:
- March 1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
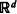 is developed and used to derive the density when
is developed and used to derive the density when 
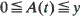 where
where 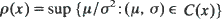 has a unique minimum on [0,
has a unique minimum on [0, 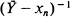 where
where 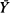 is the mean of the sample values overshooting
is the mean of the sample values overshooting 