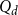Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52666 results in Statistics and Probability
Allowing for shocks in portfolio mortality models
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 27 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2022, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Extended generator and associated martingales for M/G/1 retrial queue with classical retrial policy and general retrial times
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2022, pp. 206-213
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of data in sustainability assessment of urban mobility policies
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 4 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2022, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Subgraph densities in a surface
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2022, pp. 812-839
-
- Article
- Export citation
ABO blood group and risk of malaria during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymptotics of quasi-stationary distributions of small noise stochastic dynamical systems in unbounded domains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 64-110
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Use of a non-probabilistic online panel as a control group for case–control studies to investigate food and waterborne outbreaks in Lower Saxony, Germany
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Whole-genome sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for prediction of drug resistance
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Combining antibody markers for serosurveillance of SARS-CoV-2 to estimate seroprevalence and time-since-infection
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PHASE-TYPE DISTRIBUTIONS FOR CLAIM SEVERITY REGRESSION MODELING
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 417-448
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A NEW MULTIVARIATE ZERO-INFLATED HURDLE MODEL WITH APPLICATIONS IN AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 393-416
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of transmission routes of COVID-19 cluster infections in Gangwon Province, Korea
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inferring SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding into wastewater relative to the time of infection
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Household clusters reveal household- and variant-specific properties of SARS-CoV-2
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rabies outbreak in black-backed jackals (Canis mesomelas), South Africa, 2016
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, e137
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Input-Output Analysis
- Foundations and Extensions
-
- Published online:
- 06 January 2022
- Print publication:
- 13 January 2022
Independent sets of a given size and structure in the hypercube
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 702-720
-
- Article
- Export citation
Data trust and data privacy in the COVID-19 period
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 4 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ASB volume 52 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2022, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ASB volume 52 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2022, pp. b1-b3
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation