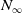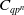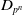Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418591 results in Open Access
(M.) CAMBRON-GOULET Partager les savoirs: pratiques orales et écrites de la philosophie dans l’Antiquité (Kaïnon – anthropologie de la pensée ancienne 23). Paris: Classiques Garnier, 2023. Pp. 269. €79. 9782406144304.
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Hellenic Studies / Volume 144 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 288-290
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Frank Gerits. The Ideological Scramble for Africa: How the Pursuit of Anticolonial Modernity Shaped a Postcolonial Order, 1945–1966. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2023. 318 pp. Illustrations. $67.95. Hardback. ISBN: 9781501767913.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 1119-1120
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The tension between democracy and populism: an empirical test of Canovan's claims of the two faces of democracy
-
- Journal:
- Italian Political Science Review / Rivista Italiana di Scienza Politica / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 240-247
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PDJ volume 39 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the rate of convergence for an α-stable central limit theorem under sublinear expectation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 209-233
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Incidence, pathophysiology, and treatment of failing Fontan after the total cavopulmonary connection
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 11 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 2406-2413
-
- Article
- Export citation
A queue with independent and identically distributed arrivals
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 319-346
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Acute Vertebral Artery Dissection in the Context of Bilateral Duplicated Vertebral Arteries
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 309-310
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ETS volume 44 issue 11 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 11 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Pathways to Peace
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 712-719
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gabriella Mazzon(ed.), Language contact and the history of English: Processes and effects on specific text-types (Austrian Studies in English 107). Berlin: Peter Lang, 2023. Pp. 256. ISBN 9783631846629.
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 173-181
-
- Article
- Export citation
Civilising loss of control? The role of criminal justice gatekeepers
-
- Journal:
- Legal Studies / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 612-630
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The combinatorics of
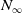 $N_\infty$ operads for
$N_\infty$ operads for 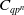 $C_{qp^n}$ and
$C_{qp^n}$ and 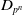 $D_{p^n}$
$D_{p^n}$
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 50-66
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
De-risking Death-traps in Uncontrolled Industrialization: Factory Act and Industrial Health and Safety in Republican China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Chinese History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Two hundred and twenty-nine cases of bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis with and without antegrade pulmonary blood flow, a single-center experience
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 1951-1955
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neurological Events Following COVID-19 Vaccination: Does Ethnicity Matter?
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 517-520
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
No sustained mean velocity in the boundary region of plane thermal convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 996 / 10 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, A49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Khalid Zairi, dir. Mora est là: Une obligation de mémoire (Mora Is Here: An Obligation to Remember). 2023. 87 minutes. Arabic, Tamazight, French, with English subtitles. ZK Productions. No price reported.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2024, pp. 1178-1179
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A semantic visual SLAM based on improved mask R-CNN in dynamic environment
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation