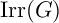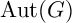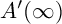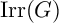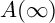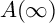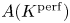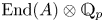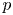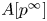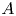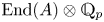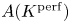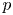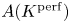Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419606 results in Open Access
Painting for a Living in Tudor and Early Stuart England. By Robert Tittler. 235mm. Pp 306, 15 b/w ills. The Boydell Press, Woodbridge, 2022. isbn 9781783276639. £70 (hbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Antiquaries Journal / Volume 103 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 454-455
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 153 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
NPS volume 51 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Nationalities Papers / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Utility of a pharmacist-managed Anticoagulation Program in patients with congenital heart disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 628-633
-
- Article
- Export citation
Decrease of left ventricular function measured by speckle-tracking echocardiography based on systemic lupus erythematosus severity in children
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 624-627
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding Sharia Processes: Women’s Experiences of Family Disputes. By Farrah Ahmed and Ghena Krayem. London: Hart Publishing, 2022. Pp. 200. £70.00 (cloth); £34.49 (paper); open access (digital). ISBN: 9781509949489. URL: https://www.bloomsburycollections.com/monograph?docid=b-9781509920761.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Religion / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 485-488
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analysis of genetic divergence, principal component, correlation and path coefficient for quantitative traits of Gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii) in the north eastern region, India
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 229-236
-
- Article
- Export citation
Notes on Article Contributors
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 249-251
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXTENSIONS OF CHARACTERS IN TYPE D AND THE INDUCTIVE MCKAY CONDITION, I
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 252 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 906-958
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Brains and Minds
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cova Dones: a major Palaeolithic cave art site in eastern Iberia
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Recessive Pathogenic GMPPB Variants Cause a Childhood Onset Myasthenic Syndrome Responsive to Pyridostigmine
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 595-597
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
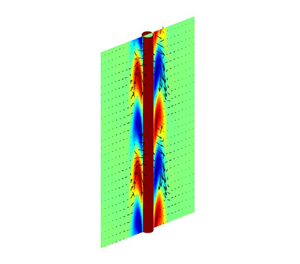
Local linear stability of plumes generated along vertical heated cylinders in stratified environments
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, A1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Freedom of Religion: An Ambiguous Right in the Contemporary European Legal Order. Edited by Hedvig Bernitz and Victoria Enkvist. London: Hart Publishing, 2020. Pp. 224. £80.00 (cloth); £39.99 (paper); open access (digital). ISBN: 9781509935864. URL: https://www.bloomsburycollections.com/monograph?docid=b-9781509935895.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Religion / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 492-494
-
- Article
- Export citation
Concepts of Actionability in Precision Oncology
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 5 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 1349-1360
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deconsecration: Symbolic Sanctions, “Courts of Honour,” and the Cleansing of Denmark’s Who’s Who After the German Occupation, 1940–1945
-
- Journal:
- Enterprise & Society / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 1049-1078
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Why A-Level Philosophy Could Do with Mary Midgley
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perfect points of abelian varieties
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 159 / Issue 11 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 2261-2278
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Canadian Cases in Private International Law in 2022
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Yearbook of International Law / Annuaire canadien de droit international / Volume 60 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 411-445
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
NPS volume 51 issue 5 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Nationalities Papers / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation