Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1397631 results in Open Access
On
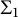 $\Sigma _1$-definable closed unbounded sets
$\Sigma _1$-definable closed unbounded sets
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Control theorems for Hilbert modular varieties
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 530-549
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
BJN volume 133 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2025, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mineralogy, petrology and geochemistry of pegmatites: Alessandro Guastoni memorial issue
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, p. 641
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Strengthening Global Health Security Under the Biden-Harris Administration
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / Spring 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 184-187
- Print publication:
- Spring 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
BJN volume 133 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2025, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Constraints on iron silicide formation from a fulgurite from Southwick, Massachusetts, USA
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Right to Work or Right to Vote? Labor Policy and American Democracy
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late positive potentials elicited by negative self-referential processing predict increases in social anxiety, but not depressive, symptoms from age 11 to age 12
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 1985-1995
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular mechanisms of the GABA type A receptor function
-
- Journal:
- Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics / Volume 58 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, e3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Viroporins: discovery, methods of study, and mechanisms of host-membrane permeabilization
-
- Journal:
- Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics / Volume 58 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Products of commutators in matrix rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 512-529
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zirconolite CaZrTi2O7 from the Kovdor phoscorites and carbonatites, Kola Alkaline Province: composition, recrystallisation and thermal expansion
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Paleomagnetic data from volcanic rocks in the southern Central Andes of Argentina and their implications for tectonics and geomagnetic field behavior
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 124 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 153-170
-
- Article
- Export citation
The PANDEM-2 Simulation Exercise: Training the Coordinated Response to a Large-Scale Pandemic in 2 European Public Health Emergency Operations Centers
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Urban temporal infrastructures in nineteenth-century Paris
-
- Journal:
- Urban History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2025, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PRESENTING INFINITESIMAL q-SCHUR ALGEBRAS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 257 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2025, pp. 134-155
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tamar Summons the Church to Account: Resisting Patriarchal (and Ecclesial) Impunity in 2 Samuel 13:21
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2025, pp. 361-378
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Crucible: Lessons Learned from Previous Centuries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2025, pp. 450-459
-
- Article
- Export citation
Violence and Representation in the Arab Uprisings. By Benoît Challand. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. 462p. $105.00 cloth, $34.99 paper.
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2025, pp. 402-403
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
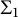





















 be a commutative ring containing a primitive
be a commutative ring containing a primitive 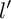
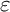
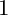
 over
over  form an ascending chain of subalgebras of the
form an ascending chain of subalgebras of the  , which are useful in studying representations of the Frobenius kernel of the associated quantum linear group. Let
, which are useful in studying representations of the Frobenius kernel of the associated quantum linear group. Let  be the quantized enveloping algebra of
be the quantized enveloping algebra of 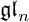
 . There is a natural surjective algebra homomorphism
. There is a natural surjective algebra homomorphism 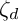
 to
to  . The map
. The map 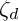
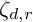
 to
to  , where
, where  is a certain Hopf subalgebra of
is a certain Hopf subalgebra of  , which is closely related to Frobenius–Lusztig kernels of
, which is closely related to Frobenius–Lusztig kernels of  . We give the extra defining relations needed to define the infinitesimal
. We give the extra defining relations needed to define the infinitesimal  as a quotient of
as a quotient of  . The map
. The map 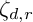
 , where
, where  is the modified quantum algebra associated with
is the modified quantum algebra associated with  . We also give a generating set for the kernel of
. We also give a generating set for the kernel of 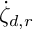
 -modules over a field of characteristic
-modules over a field of characteristic 