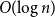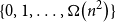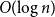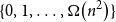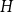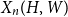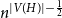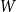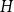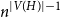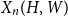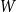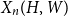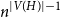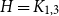Refine search
Actions for selected content:
48284 results in Computer Science
ROB volume 41 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ROB volume 41 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation

Software Engineering
- Basic Principles and Best Practices
-
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
A bipartite version of the Erdős–McKay conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, pp. 465-477
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The frequency and content of televised UK gambling advertising during the men’s 2020 Euro soccer tournament
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fluctuations of subgraph counts in graphon based random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, pp. 428-464
-
- Article
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp iv-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
6 - Design and Architecture
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 142-171
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Introduction
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 1-23
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
2 - Software Development Processes
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 24-63
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
References
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 325-336
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Notes
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 314-324
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Brief Contents
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - Static Checking
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 203-221
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp vii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp xv-xviii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - Use Cases
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp 125-141
-
- Chapter
- Export citation