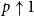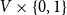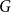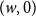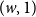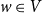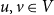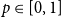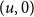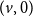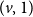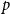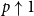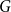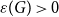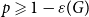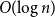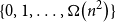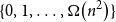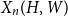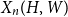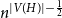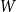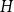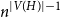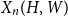Refine search
Actions for selected content:
48274 results in Computer Science
Contents
-
- Book:
- Exponential Families in Theory and Practice
- Published online:
- 25 November 2022
- Print publication:
- 15 December 2022, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - One-parameter Exponential Families
-
- Book:
- Exponential Families in Theory and Practice
- Published online:
- 25 November 2022
- Print publication:
- 15 December 2022, pp 1-47
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The bunkbed conjecture holds in the
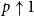 $p\uparrow 1$ limit
$p\uparrow 1$ limit
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2022, pp. 363-369
-
- Article
- Export citation
Witness statements and the technologies of memory: A conversation between Heba Y. Amin, Anthony Downey, Helene Kazan, Naeem Mohaiemen, and Susan Schuppli
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Memory, Mind & Media / Volume 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2022, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Complexity Science
- The Study of Emergence
-
- Published online:
- 13 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 17 November 2022
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
A Gaussian process state-space model for sea surface temperature reconstruction from the alkenone paleotemperature proxy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Data Science / Volume 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2022, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Large-Scale Convex Optimization
- Algorithms & Analyses via Monotone Operators
-
- Published online:
- 12 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2022

Gillespie Algorithms for Stochastic Multiagent Dynamics in Populations and Networks
-
- Published online:
- 12 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 05 January 2023
-
- Element
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reviewing the concept of design frames towards a cognitive model
-
- Journal:
- Design Science / Volume 8 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ROB volume 41 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ROB volume 41 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation

Software Engineering
- Basic Principles and Best Practices
-
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
A bipartite version of the Erdős–McKay conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, pp. 465-477
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The frequency and content of televised UK gambling advertising during the men’s 2020 Euro soccer tournament
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fluctuations of subgraph counts in graphon based random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, pp. 428-464
-
- Article
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- Software Engineering
- Published online:
- 09 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 December 2022, pp iv-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation