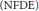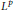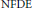Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
127 results in 47Hxx
A HYPERSTABILITY RESULT FOR THE CAUCHY EQUATION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / February 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2013, pp. 33-40
- Print publication:
- February 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A RANGE PROPERTY RELATED TO NON-EXPANSIVE OPERATORS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematika / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2013, pp. 232-236
- Print publication:
- January 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE FIXED POINT PROPERTY IN DIRECT SUMS AND MODULUS
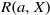 $R(a, X)$
$R(a, X)$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / February 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2013, pp. 79-91
- Print publication:
- February 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Projective dynamics of homogeneous systems: local invariants, syzygies and the Global Residue Theorem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 55 / Issue 3 / October 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2012, pp. 577-589
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
STRONG CONVERGENCE OF SOME ALGORITHMS FOR λ-STRICT PSEUDO-CONTRACTIONS IN HILBERT SPACE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 85 / Issue 2 / April 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2012, pp. 232-240
- Print publication:
- April 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
COMMON FIXED POINTS FOR SEMIGROUPS OF POINTWISE LIPSCHITZIAN MAPPINGS IN BANACH SPACES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 84 / Issue 3 / December 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2011, pp. 353-361
- Print publication:
- December 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A biharmonic equation with singular nonlinearity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / February 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2011, pp. 155-166
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
INTERSECTIONS OF HOLOMORPHIC RETRACTS IN BANACH SPACES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 89 / Issue 3 / December 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2011, pp. 297-307
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
NOTES ON GRAPH-CONVERGENCE FOR MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 83 / Issue 1 / February 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 November 2010, pp. 22-29
- Print publication:
- February 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Projectors on the Generalized Eigenspaces for Neutral Functional Differential Equations in Lp Spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / 01 February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 74-93
- Print publication:
- 01 February 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
FIXED POINT THEORY FOR VARIOUS CLASSES OF INWARD MULTIVALUED MAPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 81 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2009, pp. 1-15
- Print publication:
- February 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON FIXED POINTS OF GENERALIZED SET-VALUED CONTRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 81 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2009, pp. 16-22
- Print publication:
- February 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
NEW COINCIDENCE POINT THEOREMS IN CONTINUOUS FUNCTION SPACES AND APPLICATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 80 / Issue 1 / August 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2009, pp. 26-37
- Print publication:
- August 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON AN IMPLICIT HIERARCHICAL FIXED POINT APPROACH TO VARIATIONAL INEQUALITIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 80 / Issue 1 / August 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2009, pp. 117-124
- Print publication:
- August 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
WEAK CONVERGENCE OF AN ITERATIVE SCHEME FOR GENERALIZED EQUILIBRIUM PROBLEMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 79 / Issue 3 / June 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 May 2009, pp. 437-453
- Print publication:
- June 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nuclear and integral polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 269-280
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dual characterizations of relative continuity of convex functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 211-224
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Inscribed centers, reflexivity, and some applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 41 / Issue 3 / December 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 317-324
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The fixed point property in banach spaces whose characteristic of uniform convexity is less than 2
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / April 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 169-173
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On subsequential limit points of a sequence of iterates. II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 38 / Issue 1 / February 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 118-129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
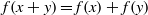
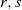
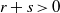
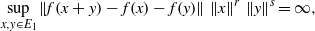
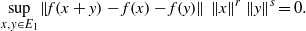

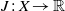
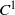
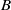
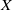
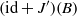
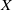
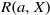
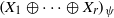

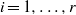
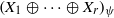
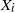
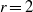
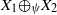
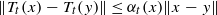 for
for