Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1381674 results in Open Access
Nutrition in the prevention and treatment of skeletal muscle ageing and sarcopenia: a single nutrient, a whole food and a whole diet approach
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 84 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 340-355
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional bursting process and turbulent coherent structure within scour holes at various development stages around a cylindrical structure
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 997 / 25 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, A61
-
- Article
- Export citation
BRIDGING BRONZE AGE SOUTH ASIA TO THE AEGEAN - (R.) Arnott Crossing Continents. Between India and the Aegean from Prehistory to Alexander the Great. Pp. xvi + 138, ills, maps. Oxford and Philadelphia: Oxbow Books, 2022. Paper, £34.99, US$49.99. ISBN: 978-1-78925-554-6.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 180-182
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary pattern trajectories in French adults of the NutriNet-Santé cohort over time (2014–2022): role of socio-economic factors
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 9 / 14 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 1184-1193
- Print publication:
- 14 November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linguistic ridicule and shifting indexical values on social media: The case of English in Hong Kong
-
- Journal:
- Language in Society / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 637-660
-
- Article
- Export citation
The mineralogical composition of the zeolitic rocks of Santorini Island and their potential use as feed additives and nutrition supplements
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 192-201
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rethinking the end of Christian Democracy
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 523-528
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stock market volatility and commodity prices
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 29 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, e45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Ceramic Mould from Vindolanda: Craft and Industry along the Roman Frontier
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
INS volume 30 issue 7 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 7 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On a weighted anisotropic eigenvalue problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, pp. 72-85
-
- Article
- Export citation
A tale of two tails: 130 years of growth at risk
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 29 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Physico-chemical properties and microstructure of bentonite in highly alkaline environments
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 72 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Polyaenus (Strat. 8.23.5) and Caesar's British Elephant
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
IMPLICIT–EXPLICIT TIME INTEGRATION METHOD FOR FRACTIONAL ADVECTION–DIFFUSION-REACTION EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 67 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The potential of enhanced germplasm for mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) improvement
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 2 / Issue 2 / August 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2024, pp. 73-80
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the self-similarity of unbounded viscous Marangoni flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 997 / 25 October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2024, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social Enterprises in Asia: A New Legal Form by Ernest Lim. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. 350 pp. Hardback: £85.00.
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Comparative Law / Volume 19 / Issue 2 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2024, pp. 399-400
-
- Article
- Export citation


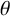
 ) and the Zimm chain solution (
) and the Zimm chain solution ( ). Numerical simulations of the viscoelastic channel flow effectively capture the nonhomogeneous regions of high viscosity at low fluid inertia (or the so-called “spatiotemporal macrostructures”), experimentally observed in the flow-instability transition of subdiffusive flows.
). Numerical simulations of the viscoelastic channel flow effectively capture the nonhomogeneous regions of high viscosity at low fluid inertia (or the so-called “spatiotemporal macrostructures”), experimentally observed in the flow-instability transition of subdiffusive flows.







