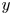Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1416829 results in Open Access
A Treason Against Goodness and an Argument for Death: Re-visiting the Trope of the “Bad Black Mother”
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Living in the edge: large terrestrial mammal and bird species traits and the ability to cope with extreme environmental conditions and human disturbance in a tropical dry forest in Colombia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Tropical Ecology / Volume 39 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, e14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jos van der Zanden. Beethoven and Greco-Roman Antiquity (Abingdon: Routledge, 2022). xvi + 272 pp. £130.00 (cloth), £38.99 (paper), £35.09 (ebook).
-
- Journal:
- Nineteenth-Century Music Review / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 433-438
-
- Article
- Export citation
Polymorphism and resistance spectrum to Magnaporthe oryzae analysis of Pi-d2 haplotypes in rice (Oryza sativa L.) resource from Yunnan province of China
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 277-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Atomic-scale deformation mechanisms at high-pressure in inderborite, CaMg[B3O3(OH)5]2(H2O)4⋅2H2O
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 473-481
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association analysis of grain mould resistance in a core collection of NPGS Ethiopian sorghum germplasm
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 201-210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Repurchases for Price Impact: Evidence from Fragile Stocks
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 60 / Issue 5 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 2334-2366
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Device closure of residual aortopulmonary window using Konar-MF occluder device: an attractive new option
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 1597-1599
-
- Article
- Export citation
First record of sand crab, Jonas kalpakkamensis Barathkumar, Das & Satpathy, 2016 (Decapoda, Brachyura, Corystidae) from the Western Indian Ocean with a key to the genus Jonas
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, e53
-
- Article
- Export citation
Management trends: Artificial intelligence, Q-Day, soft skills, work patterns, diversity, and sustainability initiatives
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 219-222
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Dogs of Tsenacomoco: Ancient DNA Reveals the Presence of Local Dogs at Jamestown Colony in the Early Seventeenth Century
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 89 / Issue 3 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 341-359
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The use of personal therapy by psychiatrists and psychiatry trainees: a systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 57-70
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prejudice and Possibility. How to Philosophize after The Culmination
-
- Journal:
- Hegel Bulletin / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 167-177
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Eating out of home in Portugal: characterisation and effects on dietary intake
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 169-181
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linear dynamics of a thick liquid layer subjected to an oblique temperature gradient
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, A32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Are Workers Effective Lawmakers?
-
- Journal:
- State Politics & Policy Quarterly / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 270-286
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maternal birth weight is an indicator of preterm delivery: the Japan environment and children’s study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 15 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ultrahigh frequency path loss prediction based on K-nearest neighbors
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 6 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 990-1000
-
- Article
- Export citation
Heikki Ikäheimo, Recognition and the Human Life-Form: Beyond Identity and Difference. New York and London: Routledge, 2022. ISBN 978-1-032-13999-9 (hbk). ISBN 978-1-032-22332-2 (pbk). Pp. 248. £130.00 (hbk). £38.99 (pbk).
-
- Journal:
- Hegel Bulletin / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 434-438
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation