Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417366 results in Open Access
Thermal behaviour of filatovite – a rare aluminoarsenate mineral of the feldspar group
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 176-184
-
- Article
- Export citation
Introduction to Everyday Internationalism: Socialist–South Connections and Mass Culture during the Cold War
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 69 / Issue S32 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Obituary: John H. M. Thornley MA, DPhil
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 887-888
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
HISTORIC LIME MORTARS COMPOSITION AND TERMINOLOGY FOR RADIOCARBON DATING—CASE STUDIES BASED ON THIN-SECTION PETROGRAPHY AND CATHODOLUMINESCENCE
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 1814-1834
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation, axial anisotropy, and formation conditions of celestine minerals from the Jabal Eghei (Nuqay) late Neogene – Pleistocene volcanic province, southeastern edge of the Sirt Basin, southern Libya: Constraints on the mineralogical geothermometer – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, p. 210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Herbage responses and animal performance of nitrogen-fertilized grass and grass-legume grazing systems
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 77-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Political change through the culture of the Radical Party (1962–89)
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 441-456
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rebels and Turcophiles? The Hungarian Protestant Clergy's Resistance against the Habsburg Counter Reformation
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 36-59
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is it Time to Include Wearable Sleep Trackers in the Applied Psychologists’ Toolbox?
-
- Journal:
- The Spanish Journal of Psychology / Volume 27 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Days alive and out of hospital for children born with single-ventricle heart disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 1445-1450
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Use of temporary tracheostomy occlusion to reduce the risk of sternal wound infection after sternotomy in congenital cardiac surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 1439-1444
-
- Article
- Export citation
Kristjánite, KNa2H(SO4)2, a new fumarolic mineral from Iceland containing the [SO4–H–SO4]3– anion in the crystal structure
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 211-217
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
List of books reviewed
-
- Journal:
- Urban History / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, p. 1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pandemic Volunteers: The Imperative for Regulations and Training
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
UHY volume 51 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Urban History / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Rare case of total anomalous pulmonary venous return into the right atrium in situs solitus
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 919-921
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neo Lekgotla laga Ramoupi, Noel Solani, André Odendaal, and Khwezi ka Mpumlwana, eds. Robben Island Rainbow Dreams: The Making of Democratic South Africa’s First National Heritage Institution. Cape Town: HSRC Press, 2021. 415 pp. Appendix. Endnotes. Select Bibliography. Index. $45.00. Paper. ISBN: 978-1-928246-29-9.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, pp. 512-513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Like we would help brothers or sisters”? Practising Solidarity with Greek Civil War Refugees in Socialist Czechoslovakia and the GDR in the Shadow of World War II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 69 / Issue S32 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 13-41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the stochastic bifurcations regarding random iterations of polynomials of the form
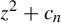 $z^{2} + c_{n}$
$z^{2} + c_{n}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 11 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 3358-3384
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
VERY LARGE SET AXIOMS OVER CONSTRUCTIVE SET THEORIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Symbolic Logic / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 455-535
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation