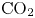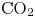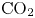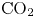Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418153 results in Open Access
Development of a regional climate change model for Aedes vigilax and Aedes camptorhynchus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Perth, Western Australia
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 8-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Variability in heritage and second language writers’ linguistic complexity: Roles of proficiency and motivational beliefs – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, p. 354
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A dynamic model of
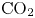 ${\rm CO}_2$ storage in layered anticlines
${\rm CO}_2$ storage in layered anticlines
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, A39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rights of Nature on the Island of Ireland: Origins, Drivers, and Implications for Future Rights of Nature Movements
-
- Journal:
- Transnational Environmental Law / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 35-60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Migration, Climate Change, and Voluntariness
-
- Journal:
- Ethics & International Affairs / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / Winter 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 452-469
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Averaging theory for heat transfer in circular hydraulic jumps with a separation bubble
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, A41
-
- Article
- Export citation
Particle-size segregation patterns in a partially filled triangular rotating drum
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, A40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Physician Management and CT Ordering in the Emergency Department for Primary Headaches
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 760-766
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Marriage, comedy, and the patristic tradition in the first Ptochoprodromic poem
-
- Journal:
- Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 253-268
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The discovery of a Romano-Punic tomb in the region of Msallata
-
- Journal:
- Libyan Studies / Volume 55 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 75-84
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Is Space Expansion the Road to Dystopia?
-
- Journal:
- Ethics & International Affairs / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / Winter 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 470-489
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Oncological and functional outcomes in T3 and T4 laryngeal cancer patients: choice for larynx preservation or total laryngectomy based on expected laryngeal function
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 672-678
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ukraine’s Strategic Interactions with the EU and Russia during the Turbulent Month of the Crimean Annexation
-
- Journal:
- Nationalities Papers / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 13-30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The new corruption crusaders: Security sector ties as an anti-corruption voting heuristic
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Estimating demand for potential disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer's disease in the UK
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 198-204
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TOPICS SURROUNDING THE COMBINATORIAL ANABELIAN GEOMETRY OF HYPERBOLIC CURVES IV: DISCRETENESS AND SECTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 256 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 785-885
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Maternal pea fiber supplementation to a high calorie diet in obese pregnancies protects male offspring from metabolic dysfunction in adulthood
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 711-718
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
OPTICALLY STIMULATED LUMINESCENCE (OSL) MORTAR DATING INTER-COMPARISON STUDY. THE SECOND ROUND OF MODIS, MORTAR DATING INTER-COMPARISON STUDY
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 1788-1800
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plumbogaidonnayite, PbZrSi3O9⋅2H2O, a new Pb-member of the gaidonnayite group from the Saima alkaline complex, Liaoning Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 185-194
-
- Article
- Export citation
“Red Housekeeping” in a Socialist Factory: Jiashu and Transforming Reproductive Labor in Urban China (1949–1962)
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation