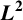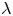Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418087 results in Open Access
Italian Studies across Disciplines: Interdisciplinarity, New Approaches, and Future Directions edited by Marco Ceravolo and Anna Finozzi, Rome, Aracne, 2022, 324 pp., €12.00 (eBook), ISBN 979-12-218-0120-0
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 529-530
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
JPA volume 97 issue 5 Cover
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
“What I Did at Vassar Stayed with Me”: Victorian Studies and Activism, a Case Study
-
- Journal:
- Victorian Literature and Culture / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / Winter 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 645-659
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Labour code, location, and migration
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 805-824
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Eustachian tube dysfunction after using different types of masks during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 755-759
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Disobedient Children, Hybrid Filiality: Negotiating Parent–Child Relations in Local Legal System in Republican China, 1911–1949
-
- Journal:
- Law and History Review / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 319-342
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effective control of refractory pulmonary hypertension with iloprost inhalation in an infant with congenital absence of the right pulmonary artery: a case report
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 690-693
-
- Article
- Export citation
JLR volume 38 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Religion / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. f1-f5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An unusual presentation: temporomandibular tissue herniation through congenital foramen of Huschke
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 811-813
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nei palchi e sulle sedie. Il teatro musicale nella società italiana dell'Ottocento by Carlida Steffan and Luca Zoppelli, Rome, Carocci, 2023, 344 pp., €32.00 (paperback), ISBN 978-88-290-1993-9
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy / Volume 29 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 531-532
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
APPROXIMATE PRICING OF DERIVATIVES UNDER FRACTIONAL STOCHASTIC VOLATILITY MODEL
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 229-247
-
- Article
- Export citation
A WEIGHTED
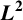 $\boldsymbol {L}^{\boldsymbol {2}}$ ESTIMATE OF COMMUTATORS OF BOCHNER–RIESZ OPERATORS FOR HERMITE OPERATOR
$\boldsymbol {L}^{\boldsymbol {2}}$ ESTIMATE OF COMMUTATORS OF BOCHNER–RIESZ OPERATORS FOR HERMITE OPERATOR
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 116 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 308-330
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of tip speed ratio on coherent dynamics in the near wake of a model wind turbine
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, A34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Response by Brittney Elizabeth Stoneburg for the presentation of the 2022 Pojeta award of the Paleontological Society
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, p. 1160
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Presentation of the 2022 Strimple Award to Joseph Koniecki
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 1147-1148
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
First occurrence of well-preserved Ordovician trilobites of the family Olenidae from Africa
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 98 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 634-643
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
AN ALGEBRAIC PROOF OF COMPLETENESS FOR MONADIC FUZZY PREDICATE LOGIC MMTL∀ – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- The Review of Symbolic Logic / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, p. 1264
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Moving on with (social) cognition in idiopathic cervical dystonia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 464-470
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The People’s Intervention: How #BlackLivesMatter Circumvented a Culture of Congruent Criminal Justice Policies in American States
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Race, Ethnicity and Politics / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, pp. 123-156
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation