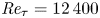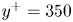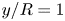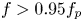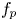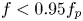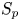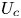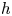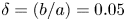Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418748 results in Open Access
THG volume 26 issue 3 Cover
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Maternal postnatal depressive symptoms and children’s internalizing problems: The moderating role of mother–infant RSA synchrony
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 1776-1788
-
- Article
- Export citation
Political Censorship in British Hong Kong: Freedom of Expression and the Law (1842−1997) by Michael Ng. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. 228 pp. Hardcover: £29.99 / HK$39.99
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Comparative Law / Volume 18 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 449-450
-
- Article
- Export citation
English Landscapes and Identities: Investigating Landscape Change from 1500 BC to AD 1086. Chris Gosden, Chris Green, Anwen Cooper, Miranda Creswell, Victoria Donnelly, Tyler Franconi, Roger Glyde, Zena Kamash, Sarah Mallet, Laura Morley, Daniel Stansbie, and Letty ten Harkel. 2021. Oxford University Press, Oxford. xxiv + 470 pp. $110.00 (hardcover), ISBN 978-0-19-887062-3.
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 88 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 613-615
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alida C. Metcalf, Mapping an Atlantic World, circa 1500 Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2020. Pp. 224. ISBN 978-1-4214-3852-8. $57.00 (hardback).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 597-598
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geoarchaeology and Coastal Morphodynamics of Harbor Key (8MA15): Indigenous Persistence at a Partially Inundated Native Shell Mound Complex in Tampa Bay, Florida
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 88 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 531-553
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Suspensions of viscoelastic capsules: effect of membrane viscosity on transient dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, A13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reproductive behaviour of the branchial ectoparasite Bopyrus crangorum (Isopoda: Bopyridae) following ecdysis of the host Palaemon serrifer (Caridea: Palaemonidae)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e67
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
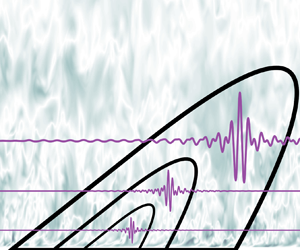
Self-similar, spatially localized structures in turbulent pipe flow from a data-driven wavelet decomposition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Expectations and perspectives of cognitive behavioural therapy for childhood anxiety and related disorders
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 65-77
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The influence of bandwidth on the energetics of intermediate to deep water laboratory breaking waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, A11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
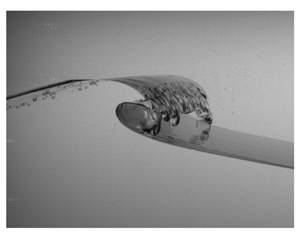
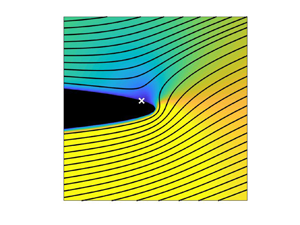
On the flow past ellipses in a Hele-Shaw cell
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Therapists’ beliefs about excessive reassurance seeking and helping manage it: does experience play a role?
-
- Journal:
- The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist / Volume 16 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GEORGE FINLAY IN EGYPT AND SWITZERLAND: NINETEENTH-CENTURY TRAVEL, SCHOLARSHIP AND SOCIAL NETWORKS
-
- Journal:
- The Antiquaries Journal / Volume 103 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 363-387
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Instrumentally Inclusive: The Political Psychology of Homonationalism
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 118 / Issue 3 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 1360-1378
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The establishment of the invasive non-native macroalga Sargassum muticum in the north of Scotland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An improved cultivation device for appendicularians with notes on the biology of Fritillaria sp. collected in Sagami Bay, Japan
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e68
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
COVID-19 as an Accelerator of the Implementation of Emergency Medical Teams Initiative in the AFRO Region
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e489
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ethical Growth in History: Good News and Bad
-
- Journal:
- The Review of Politics / Volume 85 / Issue 4 / Fall 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 567-570
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessing past versus present severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection: A survey of criteria for discontinuing precautions in asymptomatic patients testing positive on admission
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 237-240
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation