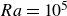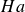Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419506 results in Open Access
VASSILIS EVANGELIDIS, The Archaeology of Roman Macedonia. Urban and Rural Environments. Oxford: Oxbow Books, 2022. Pp. xvi + 223. isbn 9781789258011 (pbk). £39.50.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
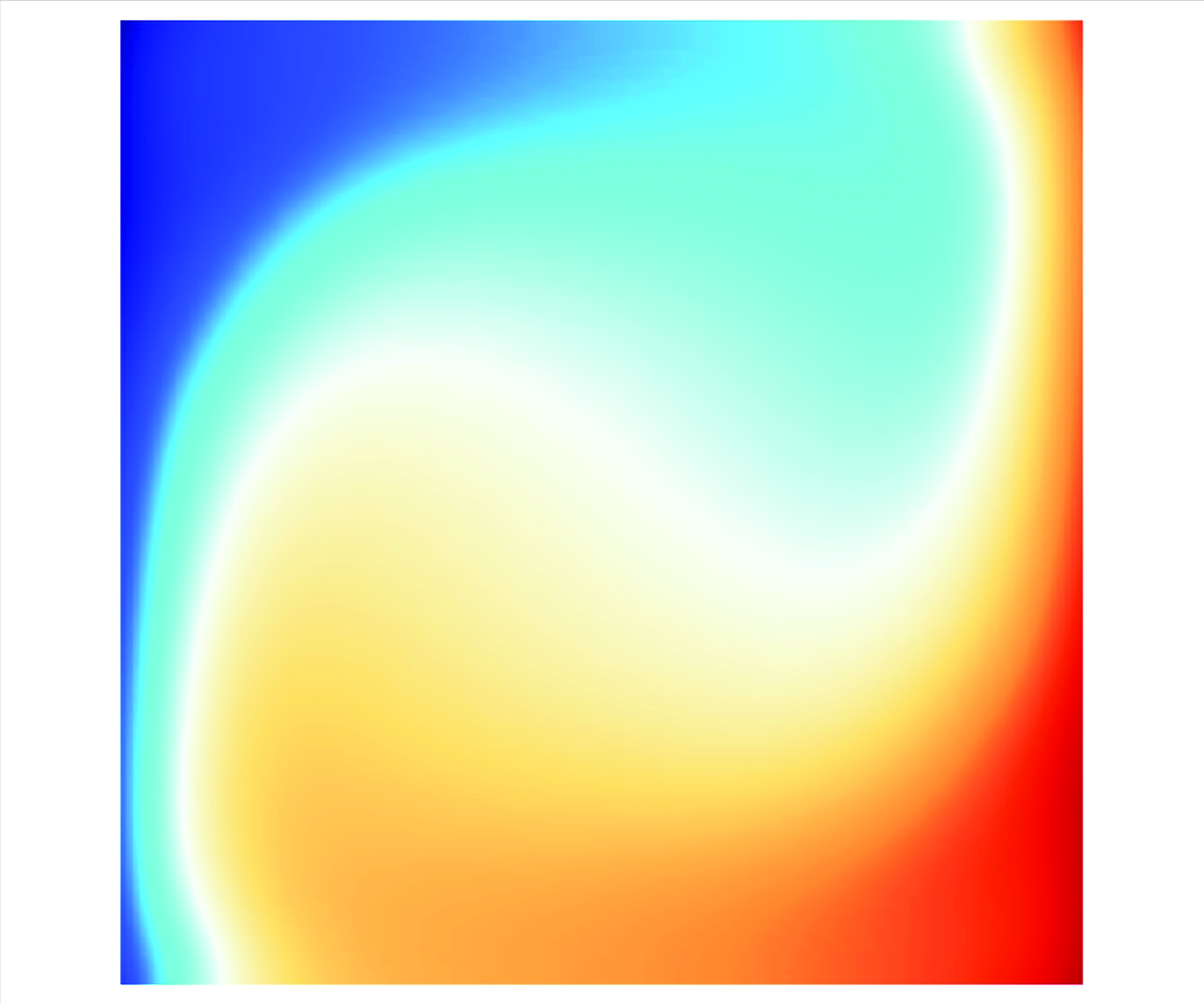
Controlling heat transport and flow structure in vertical convection using the thermoelectric effect
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hospital onset bacteremia and fungemia should be a pay-for performance measure: a pro/con debate
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 9 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 874-879
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Near-inertial echoes of ageostrophic instability in submesoscale filaments
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SAMUEL AGBAMU, Restorations of Empire in Africa: Ancient Rome and Modern Italy’s African Colonies. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2024. Pp. viii + 301. isbn 9780192848499 (hbk). £90.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
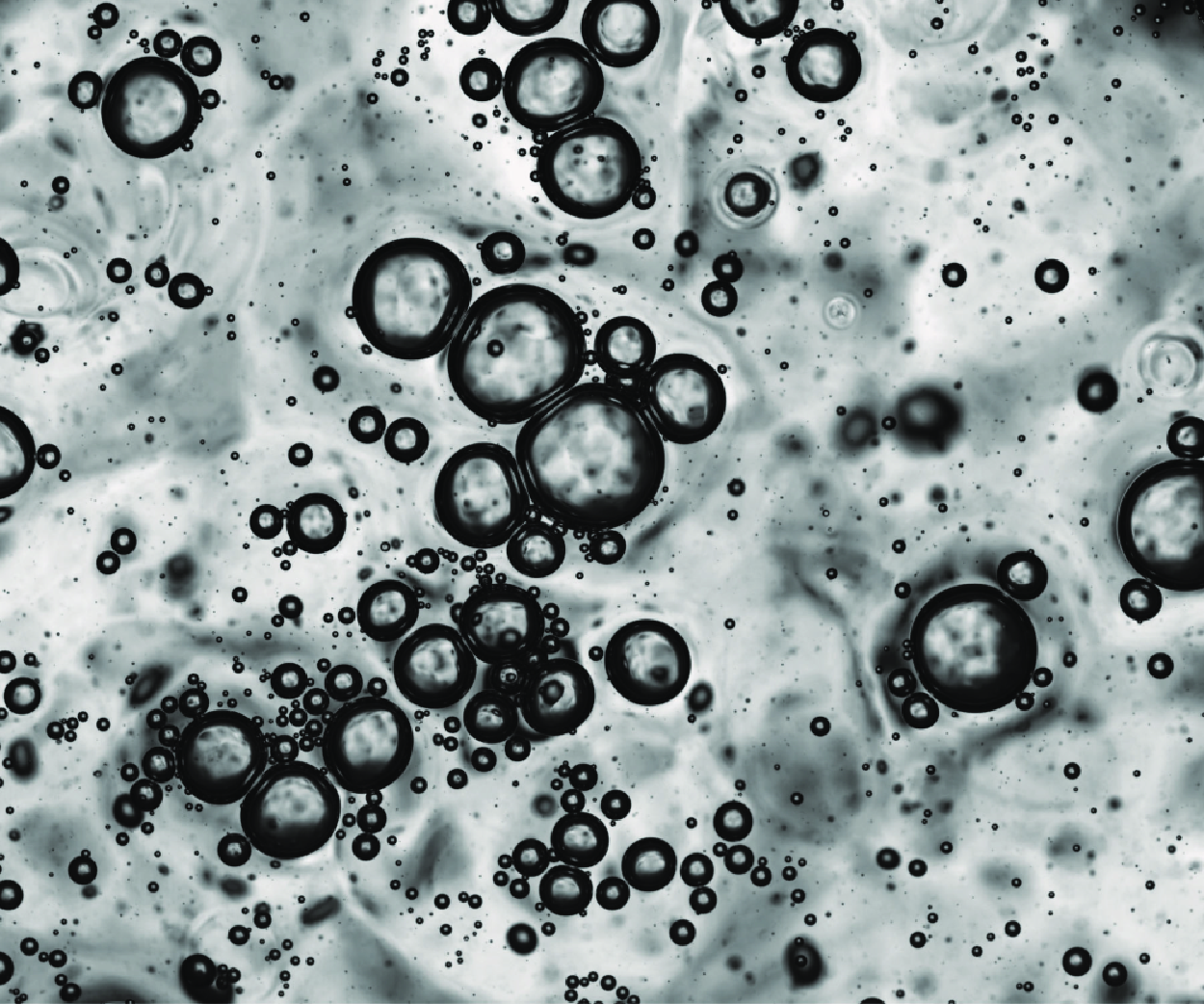
Linking emitted drops to collective bursting bubbles across a wide range of bubble size distributions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Wave- and potential-driven instabilities in orbital pilot-wave dynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Favorable tax treatment of older workers in general equilibrium
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 29 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, e119
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shlomo Sand. A Brief Global History of the Left. Polity Press, Cambridge [etc.] 2024. 264 pp. € 20.40. (E-book: € 15.99.)†
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 178-182
-
- Article
- Export citation
ALISON KEITH and MICAH Y. MYERS (Eds), Vergil and Elegy (Phoenix supplementary volume 60). Toronto, Buffalo and London: University of Toronto Press, 2023. Pp. vii + 500. isbn 9781487547950 (hbk); 9781487547967 (epub); 9781487547998 (pdf). £80.00/$115.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Early Exposure to Neurosurgery: Assessment of Perceptions, Mentorship and Competence on Medical Student Interest
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chimney instability of rotating Leidenfrost drops
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factors Affecting Separation Anxiety Disorder in Adolescent Earthquake Survivors: The Case of Kahramanmaraş Earthquakes (2023)
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, e191
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anarchisme en Méditerranée orientale et occidentale (1860–1920). Dir. par Isabelle Felici et Costantino Paonessa. Atelier de création libertaire, Lyon 2024). 191 pp. Maps. € 12.00.
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 189-192
-
- Article
- Export citation
A New Documentary History of Hong Kong, 1945–1997 Edited by Florence Mok and Fung Chi Keung Charles. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press, 2025. 428 pp. HK$280.00 (pbk). ISBN 9789888876822
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 263 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 872-873
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evolution of a family of vortex rings with zero circulation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, A29
-
- Article
- Export citation
EIVIND HELDAAS SELAND, A Global History of the Ancient World: Asia, Europe and Africa before Islam. London and New York: Routledge, 2022. Pp. 160, illus., maps. isbn 9780367695545. £37.99. - RAIMUND SCHULZ, Welten im Aufbruch: Eine Globalgeschichte der Antike. Stuttgart: Klett-Cotta, 2025. Pp. 495, illus., maps. isbn 9783608988031. £38.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
BRAM L. H. TEN BERGE, Writing Imperial History: Tacitus from Agricola to Annales. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2023. Pp. x + 411. isbn 9780472133437 (hbk). £69.00/$80.00.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparing comparatives: appropriateness ratings of synthetic, analytic and double comparatives in American and British English
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GUY MACLEAN ROGERS, For the Freedom of Zion: The Great Revolt of Jews against Romans, 66–74 CE. New Haven and London: Yale University Press, 2021. Pp. xv + 721, illus., maps. isbn 9780300248135. £25.00/$37.50.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation