Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1417116 results in Open Access
Gender-based provisions in mental health legislation: a review of English language jurisdictions
-
- Journal:
- Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 50-56
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Elizabeth Carolyn Miller. Extraction Ecologies and the Literature of the Long Exhaustion New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 2021. Pp. 304. $99.95 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 957-959
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nutritional interventions in patients with burn injury: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomised clinical trials
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1317-1324
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Unified Canon? Latin American Graduate Training in Comparative Politics
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 98-123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Francis Fallon and Gavin Hyman (eds.). Agnosticism: Explorations in Philosophy and Religious Thought (Oxford – New York: Oxford University Press 2020). Pp. x + 218. £78.00 (Hbk). ISBN: 9780198859123.
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of skin thickness on electromagnetic dosimetry analysis of a human body model up to 100 GHz
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 8 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1373-1380
-
- Article
- Export citation
RATIONAL REPRESENTATIONS AND RATIONAL GROUP ALGEBRA OF VZ
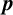 $\boldsymbol {p}$-GROUPS
$\boldsymbol {p}$-GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 118 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1-30
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Joshua Sijuwade. Analytic Theism: A Philosophical Investigation (New York: Routledge Press, 2024). Pp. 1–647. £135.00 (Hbk ISBN 978-1-032-26359-2
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
David Cressy. Shipwrecks and the Bounty of the Sea Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2022. Pp. 336. $41.99 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 888-889
-
- Article
- Export citation
Result lexicalization with manner verbs in French: an experimental investigation of the material/product alternation and the packaging of meaning
-
- Journal:
- Journal of French Language Studies / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 457-482
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Did the pandemic lead to a change in attitudes towards cCBT? A service evaluation looking at the impact of the pandemic on practitioner beliefs regarding the routine use of cCBT within an NHS Talking Therapies Service
-
- Journal:
- The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist / Volume 17 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Earliest Ancient Maya salt production in southern Belize: excavations at Jay-yi Nah
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Surgical management of a giant left coronary artery aneurysm mimicking cardiac mass
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 11 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 2471-2473
-
- Article
- Export citation
Natasha Szuhan. The Family Planning Association and Contraceptive Science and Technology. Medical and Biomedical Sciences in Mid-Twentieth-Century History Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, 2022. Pp. 294. $139.99 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 968-969
-
- Article
- Export citation
Claudio Lomnitz, Sovereignty and Extortion: A New State Form in Mexico. Durham: Duke University Press, 2024. Tables, notes, bibliography, index, 240 pp.; hardcover $98.95, paperback $25.50.
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chengba: the Dangqu City of the Han Dynasty in south-west China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Estimation of dominance genetic effects on pre-weaning efficiency-related traits in Baluchi sheep
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 283-289
-
- Article
- Export citation
Janet Schrunk Ericksen. Reading Old English Biblical Poetry: The Book and the Poem in Junius 11 Toronto Anglo-Saxon Series. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2021. Pp. 234. $71.00 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 896-898
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE SHARP BOUND OF THE SECOND HANKEL DETERMINANT OF LOGARITHMIC COEFFICIENTS FOR STARLIKE AND CONVEX FUNCTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 1 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2024, pp. 163-171
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation